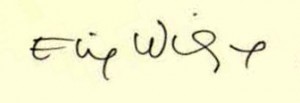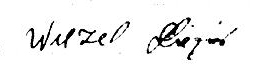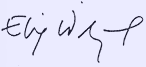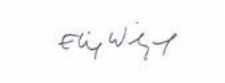Posts Tagged ‘Miklos Grüner’
Wednesday, March 7th, 2012
By Carolyn Yeager
copyright 2012 Carolyn Yeager
Elie Wiesel questioned under oath in a California courtroom in 2008:
Q. And is this book Night that you wrote a true account of your experience during World War II?
A. It is a true account. Every word in it is true.

Elie Wiesel manning his table at a Jewish book fair in Austin, TX, 2006. The new translation of Night by his wife Marion had come out in January of that year, and it was immediately chosen for Oprah Winfrey’s book club.
In Part One, I established that the decision to rebrand Night into an autobiography was the reason for a new translation, in which necessary changes could be made to better ‘fit’ the story both to the real Elie Wiesel and the known facts of the Hungarian deportation.
When the 2006 translation came out, with its new classification to “autobiography,” questions arose from some circles. Responding to these questions, Edward Wyatt wrote an article in the NewYork Times on Jan. 19, 2006, in which he quoted Jeff Seroy, senior vice president at Farrar, Straus & Giroux, parent company of Night publisher Hill & Wang, as strongly denying that changes were made to bring the book more in line with the facts. “Nonsense,” said Seroy. “Some minor mistakes crept into the original translation that were expunged in the new translation. But the book stands as a record of fact.”
Blaming the Translator
“Mistakes in the original translation” can only mean mistakes by Stella Rodway, the original translator! But we have already shown that Stella Rodway faithfully reproduced the French La Nuit, which was Wiesel’s own work. The author and publisher are casting these changes as translation errors to divert attention away from Elie Wiesel’s own errors—part of their campaign to pass Night off from now on as “a record of fact.”

Publisher Jeff Seroy, center, with writer Brad Gooch to his left, Doug Stumps on his right .
A record of fact it isn’t
When I ended Part One, Eliezer and Father were still in the train car on their way to Buchenwald. You will recall that the Yiddish, the French and thus the original English version of Night specified the trip took 10 days and 10 nights from Gleiwitz (on the former German/Polish border) to Buchenwald. Since we know from standard historical sources1 that the prisoners were evacuated from Monowitz on Jan. 18 and arrived in Gleiwitz the next day, Jan. 19; and since according to the description in Night itself, they spend three days in Gleiwitz (Jan. 20-22), this would make their day of arrival February 1, 1945. But in Night, Father’s death takes place the night of Jan. 28-29, three days before they arrived! This is why Marion Wiesel removed the number 10 in her new translation, leaving the number of days and nights undetermined.
A strange detail that actually belongs in Part One is on page 87 of the original Night. Eliezer remarks, after his and his Father’s deliberations and final decision to go on the march: “I learned after the war the fate of those who had stayed behind in the hospital. They were quite simply liberated by the Russians two days after the evacuation.” The evacuation, as we all know, was on the 18th. We also know the Russians did not arrive on the 20th of January! The actual liberation day is January 27. What possessed Wiesel to write this? Well, because it was in Un di velt: “Two days after we had left Buna, the Red Army occupied the camp. All the sick had stayed alive.”
From the point in the story of Eliezer and Father’s arrival at Buchenwald there are no significant changes made by Marion Wiesel to the original French and English versions. But there is much in all the versions that differs strikingly from the “official holocaust history” as written by acknowledged official chroniclers such as Danuta Czech. So I will continue with comparisons between Night and “official history,” along with some very significant changes made from Un di velt hot geshvign to Wiesel’s edited French La Nuit.
Arrival at Buchenwald: 26 Jan. or 1 Feb.?
 Danuta Czech, in her Auschwitz Chronicle1, records that on January 26,
Danuta Czech, in her Auschwitz Chronicle1, records that on January 26,
A transport with 3,987 prisoners from Auschwitz auxiliary camps reaches Buchenwald. There are 52 dead prisoners in the transport. 115 prisoners die on the day of arrival. Their corpses are delivered to the autopsy room. (P 801)
This is the transport that carried Lazar and Abraham Wiesel/Viezel, Miklos (Nikolaus) Grüner and all of the inmates of Monowitz whose names are on the transport list.2 According to Czech, the Monowitz prisoners began their march on the evening of January 18, 1945, with “divisions of nurses placed between the columns” of 1000 each (P 786), arriving at Gleiwitz Camp the following evening. On Jan. 21 “they are loaded in open freight cars with other prisoners from Auschwitz who have arrived in Gleiwitz.” (P 788) From Jan. 21 to Jan. 26 is five days of travel … not ten, as Wiesel wrote in Night.
The narrative in Night gives us a date of Jan. 22 for the boarding of the train, one day later than Czech. And while Night gives the number of days on the train (10), it does not name the date of arrival.
Hilda Wiesel says her father died on arrival
Totally contradicting what is written in Night, Hilda Wiesel Kudler, Elie’s oldest sister, in her testimony for the Shoah Foundation in 1995, said she learned from her brother that their father died as he stepped off the train.

Hilda Wiesel Kudler, in France, giving her videotaped testimony to the Shoah Foundation
And I said, where is father? And he replied, he’s gone back to Sighet; he[Elie] didn’t want to tell me [that he was dead]. And I repeated, but where is he? And he insisted he was at Sighet. And I said, look, I want you to tell me the truth. Because he knew the date of my father’s death. You know, they did a long march3 from Auschwitz, then they put them on the train to go to Buchenwald; he died gasping for air; when he stepped off the train, he died gasping for air; at Buchenwald. But he[Elie] knew the date.
From this, we can better understand something about Elie Wiesel—that he has never had a problem with making up stories that “sound better” than the truth. But, if Hilda is correct in her recall, and if their father really was one of the 115 inmates who Danuta Czech reports died on the day of arrival, then Wiesel’s long, melodramatic story of watching his father sicken and die over a ten-day period in Night is fiction. All of it—including his father being whacked on the head by a cruel “officer” in the barracks.
The day of arrival for this transport is Jan. 26, but according to the timeline in Night, it arrives on Feb. 1. Either way, it doesn’t correspond to the date of Jan. 28 that Wiesel, for reasons unknown, selected as the date his fictional Father died.
You might also be interested to know that Hilda is named Deborah in Un di velt; the name Hilda is never used. It was Wiesel who changed it to Hilda in La Nuit.
Un di Velt says Father dies a week after arrival in Buchenwald, Night says 8-10 days … yet it is January 28 … or is it the 18th Day of Shevat?
Regular readers of this blog will know this already, but it bears repeating yet again: there is no Shlomo Wiesel in the official history or in the records who fits the profile of “Father” as described by Elie Wiesel in Night. There is an Abraham (sometimes shortened to Abram) Viezel who is recorded in several places—on a medical report at Auschwitz, on the transport to Buchenwald, and on a death certificate dated Feb. 2, 1945, seven (7) days after arrival. This Abraham was born Oct. 10, 1900, making him 44 years old when he died. Recall that Night gives Father’s age as 50 in 1944 (SR, P 40).
Wiesel’s description has the transport to Buchenwald arriving on Feb.1st. But that’s just the beginning. After arriving, this is the timeline given in both the original Night and Marion Wiesel’s 2006 translation:
It was daytime when I awoke. I went to look for my father. (Feb. 2nd)
[…]
On the third day after our arrival at Buchenwald, everyone had to go to the showers [his father went too-cy]. Even the sick who had to go through last. (Feb 4th) […] Struck down by dysentery, my father lay in his bunk, five other invalids with him. I sat by his side watching him … A week went by like this. (Feb. 11th or Feb. 8th depending on how you read it)
[ . . . ]
When I got down after roll call, I could see his lips trembling as he murmured something. […] Then I had to go to bed. I climbed into my bunk, above my father, who was still alive. It was January 28, 1945. (still Feb. 8 or 11) I awoke on January 29 at dawn. In my father’s place lay another invalid. They must have taken him away before dawn and carried him to the crematory.” (Feb 12th or 9th) [Stella Rodway translation, pp 107-112]
The timeline in Un di velt is not in doubt:
On the seventh or eighth day of our being in Buchenwald, the bunk-elder [should be block-elder -cy) who used to deal out bread for the whole bunk [sic], came to me. . . .
[ . . . ]
On the same day, in the evening, disaster struck. The end. During roll call. The healthy had to go out of the block in order to be counted by the S.S. men. The sick stayed in their bunks. My father and I thus stayed inside. He — because of his dysentery and I — because of my bandaged foot. Father was lying in the lowest bunk and I — in the uppermost.
[ . . . ]
After roll call, I immediately jumped down from the uppermost bunk and ran to him. He was still breathing. But — he was silent.
[ . . . ]
For a couple of hours I stayed by him and looked at his face long and well […] Then they forced me to go lie down to sleep. I climbed up to the uppermost bunk and I did not know that in the morning, on awakening, I would find my father no more.
It was the eighteenth of Shevat, 5705.
* * *
Nineteenth of Shevat. Early in the morning.
I got up and ran to my father. Another sick man was lying in his place.
I had a father no more. (pp 233-238)
Readers might be surprised to learn that the Hebrew calendar date of 18-19 Shevat, 5705 corresponds to February 1-2, 1945! How neat is that? So, in Un di velt Father dies seven days after arrival, on the very same day as Abraham Viezel died, who was officially recorded at Buchenwald with the registration number of 123488 and the Auschwitz registration number of A-7712. (However, Un di velt also says that the trip from Gleiwitz to Buchenwald took ten days, which means they could not have arrived until sometime in February. Seven days from that time would not be Feb. 2nd.)
So can we conclude from this that Abraham is Shlomo? Not necessarily. The Yiddish author reports Father’s death as occurring during the night of 18-19 Shevat (Feb. 1-2), but Elie Wiesel, author of La Nuit, says the date is Jan. 28th! Why? Who can answer that but Elie Wiesel? He certainly knows what the month of Shevat and the year 5705 means … or he could have easily found out.
Or can we conclude that Un di velt was written by Lazar Wiesel, as Nikolaus Grüner claims … that he wrote his story as a father-son relationship … and that he was perhaps not the brother of Abraham as Grüner says he was? (It’s noted on Lazar’s Buchenwald file card that his father was also in Buchenwald; his mother in Auschwitz.) Well, again, not necessarily. There are other possibilities. But I’m getting ahead of myself.
The facts are, there are problems with all of these theories; none is a perfect fit. We can ask: If Elie Wiesel is the author of Un di velt hot geshvign, why did he change so many of the underpinning facts of the story when he rewrote it in French as La Nuit? This is a real head-scratcher. We can also ask: Why did Naomi Seidman, the Jewish professor who discussed in detail some of the differences between the Yiddish book and Night, not mention the 18th of Shevat? Is it because she couldn’t find an explanation for it? Siedman, Ruth Franklin and other Jewish reviewers have never brought up some of these Yiddish to French discrepancies. They are too embarrassing a problem for them.
What we can safely say is that no matter who the author of Un di velt was … he was totally unfamiliar with the real facts of when the Monowitz prisoners arrived at Buchenwald. Was it because he was not one of them? Was it because he was not concerned about accuracy since his story was directed at a non-critical audience—a Yiddish-speaking Jewish audience? As we continue, we’ll find more mystifications, but also a few certainties.
What happens to Eliezer after Father’s death?
Wiesel writes in Night (essentially the same in all translations):
I had to stay at Buchenwald until April eleventh. I have nothing to say of my life during this period. […] I was transferred to the children’s block, where there were six hundred of us. […] I spent my days in a state of total idleness. And I had one desire—to eat. I no longer thought of my father or of my mother. (SR, P 114)
He continues that on April 10, a general evacuation of the remainder of the camp—20,000 prisoners in all, including “several hundred children”—was begun but was soon interrupted. It resumed on the 11th but was again interrupted around ten a.m. when the camp inmate “resistance movement” rose up, firing guns. And then at 6 p.m. on that same day the first American tank arrived. This corresponds pretty well with the official story, but then it goes astray.
In a November 2000 interview with Oprah Winfrey, Wiesel recalled:

Elie interviewed by Oprah in 2000.
… and we [children] were left until the end. But every day we marched to the gate anyway. I was near the gate more than five times before I was released, and each time, the gate closed just before I came to it.
Ah, we have heard this before, haven’t we? As exaggerated as it sounds, in Un di velt the author goes even further. He writes:
I didn’t even bother to try hiding myself. Let myself be born along with the stream. Tens of times I stood before the iron camp gate, on the threshold of death, and always something happened which brought us back to the block.
Un di velt continues: “If I was not killed then it is merely thanks to almightly chance. For – because of the hunger, I even wanted to go to the gate: outside the gate, they were distributing bread and marmalade.”

The front gate at Buchenwald, from the inside looking out, that Wiesel says he marched right up to “tens of times” but was always turned back!
- Liberation brings Freedom and Revenge
UdV, P 244: The first gesture of freedom: the starved men made an effort to get something to eat. They only thought about food. Not about revenge. Not about their parents. Only about bread. And even when they had satisfied their hunger—they still did not think about revenge.
SR, P 115: Our first act as free men was to throw ourselves onto the provisions. We thought only of that. Not of revenge, not of our families. Nothing but bread.
Oprah Winfrey interview: Oprah asks, “After you were liberated, what did you do?” Wiesel answers: “The first thing many of us did was reassemble to say a prayer for the dead.” (page 5)
* * * *
UdV, P 244: Early the next day Jewish boys ran off to Weimar to steal clothing and potatoes. And to rape German girls [un tsu fargvaldikn daytshe shikses]. The historical commandment of revenge was not fulfilled.
LN, P 178: Le lendemain, quelques jeunes gens coururent à Weimar ramasser des pommes de terre et des habits—et coucher avec des filles. Mais de vengeance, pas trace.
SR, P 116: On the following day, some of the young men went to Weimar to get some potatoes and clothes—and to sleep with girls. But of revenge, not a sign.
MW, P115: The next day a few of the young men ran into Weimar to bring back some potatoes and clothes—and to sleep with girls. But still no trace of revenge.
In this case, Wiesel made the change from ‘rape’ to ‘sleep with’ in La Nuit. The expression for “German girls” that we find in the Yiddish book was also removed. The term that was actually used is shikses, a word which originally meant “abomination” and which is used today as a term of contempt for all non-Jewish women. In other words, in saying daytshe shikses, the author was expressing, in rather vulgar terms, his contempt and hatred for German women. This apparently was not good for the eyes of the Goyim to see. It was changed by Wiesel in the French La Nuit, and thus it never reached our eyes until now.
Yet, the Yiddish author goes even further and decries the failure of the Jewish males to take a proper revenge, which is here envisioned as a much larger public act of retribution than the “too mild” raping of German women. (Public retribution, of course, did come later with the Nuremberg Military Tribunals.)
Eliezer is hospitalized for two weeks—April 14 to April 28
UdV P 244: Three days after liberation I became very ill; food-poisoning. They took me to the hospital and the doctors said that I was gone. For two weeks I lay in the hospital between life and death. My situation grew worse from day to day.
SR P 116: Three days after the liberation I became very ill with food poisoning. I was transferred to the hospital and spent two weeks between life and death.
MW P 115: Three days after the liberation of Buchenwald, I became very ill: some form of poisoning. I was transferred to a hospital and spent two weeks between life and death.
Three days after liberation on April 11th is April 14th. Thus, Eliezer is in the hospital from April 14 until April 28—extremely ill, close to death. In his 1995 memoir, All Rivers Run to the Sea, Elie Wiesel claims that on that day (the 14th) he was thrown a can of lard, which he apparently ate although he doesn’t remember doing so. He lost consciousness and awoke in a hospital. But the addition of this story, which is in the original Un di velt, presents serious problems for Elie Wiesel. Perhaps the hospital story had slipped his mind when he decided to claim he was one of the survivors lying on a bunk in the “famous Buchenwald liberation photograph.” Because he was in the hospital …
He cannot be in the famous Buchenwald liberation photo taken on April 16 …
I have already demolished the false claim that Wiesel is in that photograph here. But on top of that, our translator found an interview of Leo Eitinger, a Jewish Czech-born psychiatrist, by Harry James Cargas, a friend and biographer of Elie Wiesel, which contained this gem:
HJC: The same thing happened with Livia Rothkirchen at Yad Vashem as happened with you. I was there doing research on atrocity photography for my book A Christian Response to the Holocaust and saw a photo that covers a large wall, of seventeen men lying in their bunks at liberation time. I think you’ve probably seen this picture. Wiesel and Dr. Rothkirchen passed it by many times, over a several-year period, before he told her he was in that photograph. I asked Elie if I could write something about it and he said, “No.” I wrote something and showed it to him and he gave me permission to publish it.

The photo at Yad Vashem in Israel with Elie Wiesel posing in front of it in 1986 after receiving the Nobel Peace Prize in Oslo.
LE: I didn’t know Elie is in the photo.4
Cargas’ book was published in 1993, ten years after it was publicly announced that Elie Wiesel was in that photograph. Apart from the revelation that Cargas has to ask permission from Wiesel before he publishes anything about him, can you imagine that after walking by that famous photo for several years, Wiesel would finally think to say, “Oh hey, that’s me laying there, back in the shadows.”
He cannot have been present to agree to and sign the Military Questionaire on April 22 …
Much has been made by holocaust historians like Kenneth Waltzer and others I won’t name that this Fragebogen made out for Lázár Wiesel proves that Elie Wiesel was in Buchenwald. The birth date is not Elie’s; the date of arrest is not Elie’s; the signature is not Elie’s; the registration number belongs to another prisoner (Pavel Kun) who died only a month earlier; and on top of all that … Elie himself tells us in Night that he was lingering between life and death in the hospital on April 22. He was still six days away from having recovered enough to leave the hospital.
He cannot be in the photograph of the “Boys of Buchenwald” taken on April 27.
 Kenneth Waltzer also claims on his Michigan State University website that Elie Wiesel is “seen to the left” (short boy fourth from the front in left row wearing dark suit in front of the taller boy wearing a beret) in this photograph of the youths being transferred from the barracks inside Buchenwald to the former SS barracks on the outside. Why is Waltzer not paying attention to what is written in Night — that Eliezer was put in the hospital on the 14th of April, at death’s door, and remained for two weeks? One really has to wonder at the stupidity of holocaust historians. Or more likely — how stupid they think the rest of us are! See The Many Faces of Elie Wiesel.
Kenneth Waltzer also claims on his Michigan State University website that Elie Wiesel is “seen to the left” (short boy fourth from the front in left row wearing dark suit in front of the taller boy wearing a beret) in this photograph of the youths being transferred from the barracks inside Buchenwald to the former SS barracks on the outside. Why is Waltzer not paying attention to what is written in Night — that Eliezer was put in the hospital on the 14th of April, at death’s door, and remained for two weeks? One really has to wonder at the stupidity of holocaust historians. Or more likely — how stupid they think the rest of us are! See The Many Faces of Elie Wiesel.
The book’s ending: What does the long passage in Un di velt hot geshvign tell us?
UdV P 245: One fine day I got up—with the last of my energy—and went over to the mirror that was hanging on the wall. I wanted to see myself. I had not seen myself since the ghetto.
From the mirror a skeleton gazed out.
Skin and bones.
I saw the image of myself after my death. It was at that instant that the will to live was awakened.
Without knowing why, I raised a balled-up fist and smashed the mirror, breaking the image that lived within it.
And then—I fainted.
From that moment on my health began to improve.
I stayed in bed for a few more days, in the course of which I wrote the outline of the book you are holding in your hand, dear reader.
But—
Now, ten years after Buchenwald, I see that the world is forgetting. Germany is a sovereign state, the German army has been reborn. The bestial sadist of Buchenwald, Ilsa Koch, is happily raising her children. War criminals stroll in the streets of Hamburg and Munich. The past has been erased. Forgotten.
Germans and antisemites persuade the world that the story of the six million Jewish martyrs is a fantasy, and the naive world will probably believe them, if not today, then tomorrow or the next day.
So I thought it would be a good idea to publish a book based on the notes I wrote in Buchenwald.
I am not so naive to believe that this book will change history or shake people’s beliefs. Books no longer have the power they once had. Those who were silent yesterday will also be silent tomorrow. I often ask myself, now, ten years after Buchenwald:
Was it worth breaking that mirror? Was it worth it?
SR P 116: One day I was able to get up, after gathering all my strength. I wanted to see myself in the mirror hanging on the opposite wall. I had not seen myself since the ghetto.
From the depths of the mirror, a corpse gazed back at me.
The look in his eyes, as they stared into mine, has never left me.
MW P 115: One day when I was able to get up, I decided to look at myself in the mirror on the opposite wall. I had not seen myself since the ghetto.
From the depths of the mirror, a corpse was contemplating me.
The look in his eyes as he as he gazed at me has never left me.
The difference in length between the Yiddish and the English passage is the first thing that strikes us. The Yiddish writer had a lot to say in these final thoughts. He regained his “will to live” right there in the hospital. Twice he speaks of writing an outline and notes for Un di velt hot geshvign while still in his hospital bed. But there is no record by Elie Wiesel anywhere that says he did any writing in preparation for writing his “testimony” while in the camp (in fact, just the opposite), or at any time in advance of 1954.

Ilse Koch on the witness stand in 1947. She was seven months pregnant and the only woman brought before the American Military Tribunals held at Dachau.
The tragic true story of Ilse Koch is that she gave birth to one child while a prisoner of the Americans but she certainly was not allowed to raise him. She was hounded, vilified and persecuted after the war, retried by a German court in 1951 after being acquitted at the IMT, and ultimately given a life sentence—solely, it can be argued, to satisfy Jewish vengeance. She committed suicide in prison in 1967.
The Yiddish author also mentions the “six million Jewish martyrs” … in 1954. This number emerged from the Nuremberg Tribunals, but we know that claims of “six million Jewish victims” goes all the way back to the 1890’s.
All this and more was cut out for the French La Nuit (which, remember, was written by Wiesel) and the English versions which were taken from the French. As has been noted by Jewish commentators themselves, the Yiddish writer is an angry, politically-minded religious Jew who expected, or wished, the world to have been transformed by the travail of the Jews during WWII. He is bitterly disappointed. There is more in this final chapter of the Yiddish book that doesn’t appear in the French or English versions. Here is just one passage:
Dreams of truth, of freedom are false dreams for men. Visions of justice and equality are false visions for men. Man is: the struggle for bread, for meat; man is: the struggle to satisfy one’s own instincts.
Man is instinct to the core. Flesh to the core. And not heart. And not spirit. And not morality.
I learned that in Buchenwald. And what one learns in such conditions is without a doubt the truth, the purest truth. For man can really know man only in extreme conditions, when he has thrown away from himself all masks, social and psychological, and appears before us naked, as he is in truth.
In Buchenwald I saw the true face of man. The face of a human animal, which is worse than a true animal. O God, woe is you, woe is man, how trifling and puny. Ought you to even exist, if the son of Adam was made in your image!
God . . . I had ceased to believe in his existence. But despite that, I continued to believe in his evil. (UdV, P 240-41)
Was this written by Elie Wiesel? If it was, he is a man who has put on his own mask to play the game of Jewish vengeance against the goyim persecutors of his people. In other parts of Night, Wiesel writes of losing his faith in a caring God, of no longer following his religion—but later he denied that is true, even though he wrote it! But this passage in Un di velt is too passionate to dismiss as merely a passing sense of discouragement. That is, of course, unless it is just a literary construct and doesn’t reflect any truth of the author.
What does it all mean?
The title of this two-part article is “What Changes were made to Elie Wiesel’s Night, and Why.” I didn’t promise to solve the mystery of the author of Un di velt hot geshvign, but I did hope I might do so, or at least eliminate some contenders.
I confess I expected there to be more difference between the Yiddish and the French books than it turns out to be. It is now clear that La Nuit was taken directly from Un di velt, although that doesn’t mean they were written by the same person. However, that is the greater likelihood unless it can be proven otherwise. Similarly, if Elie Wiesel is the author of Un di velt, it doesn’t mean he was in the camps. The fact that the books are filled with errors argues against it.
Night is a novel
It’s difficult to come to any certainties when the material we have to work with is so internally inconsistent and when there are several versions of it—similar in some ways to the many versions of the Anne Frank Diary. But we can conclude for certain that Night only works as a novel, not as an autobiography—no matter how much the Jewish spin doctors say that a memoir, to be a work of “great literature,” must include some fictional flights of fancy. Nowhere does Night fit the facts. Even with wife Marion’s changes in 2006, it couldn’t be pulled together enough to make a convincing true-life testimony. And we know how many of these “survivor novels” there are around. It’s not like many other hopefuls didn’t have the same idea!
The Lazar-Lázár Riddle
In spite of all the above, I would like to propose a hypothetical scenario, one that I am not endorsing, for obvious reasons, but that does have the value of answering one of the more ignored aspects of this riddle, namely the way the 32-year-old Lazar Wiesel disappeared at the same time the 16-year-old Lázár Wiesel appeared. This cannot be denied. Thirty-one-year-old Lazar arrived at Buchenwald in January; sixteen-year-old Lázár left there in July. The easiest explanation for this is that Lazar wanted to have the papers of a 16-year-old Buchenwald orphan so he could be sent to France. In the confusion of the last months of the war and the immediate post-war period, this kind of thing became more possible. Such an explanation may sound a little far-fetched, but is it any harder to swallow than Elie Wiesel not having the tattoo (Auschwitz ID number) that he says he has? Or Elie Wiesel not having his own Buchenwald identification number, but “borrowing” a dead man’s (Pavel Kun, 2 years older than Elie) right before, or after, liberation? These things don’t make sense. Nor does the fact that in La Nuit Elie Wiesel wrote that his father died on Jan. 28, 1945, while in the Yiddish book that he also claims to have written as his own “testimony” the date is Feb. 2nd? Or that he wrote that the Russian Army took over the Auschwitz complex two days after its evacuation, which everyone knows is false?
Elie Wiesel even wrote in Night that his foot was operated on right before the evacuation of Auschwitz, while in his later real memoir, All Rivers Run to the Sea (pp 89-90), he flat-out recalled it as his knee, something that could not be mis-remembered. I could list many of these senseless “mistakes,” many of which I have written about in earlier articles.
There is something that doesn’t fit well into this Lazar-Lázár hypothesis, though—that is, that we have pictures of the real Elie Wiesel in France at the Jewish welfare orphanage, OSE. But how did he get through a year at Auschwitz and Buchenwald with no records of his being there … and a poor memory of what occurred and when? Did he somehow manage to attach himself to the Buchenwald transport with the stolen identity papers? But also, there are other ways he could have come to be at the Ecouis homes in France than in the children’s transport from Buchenwald. Just as there are other ways he could have come into possession of the Yiddish Un di velt without writing it himself.
Was Elie Wiesel in the camps?
My answer is still no. Wiesel could have been in some camps in some capacity under some auspices, but he is not telling the truth about what camp experience he did have. That means Hilda Wiesel Kudler is also not telling the truth but is standing by her brother. She says at the end of her bitter testimony to the Shoah Foundation, “I will not forget, and I will not forgive.” Have you ever wondered why Elie has not contributed a videotaped testimony to the Spielberg/USC Shoah Foundation library?

Elie Wiesel with his older sisters Bea (left) and Hilda (right) in Paris after the war, exact date unknown.
Wiesel’s other sister, who changed her name to Beatrice from Batia, never wrote or testified a word about it. She did go to work for Jewish organizations in Germany, however, immediately after the war, helping Jews to emigrate to wherever they wanted to go, including Palestine. The whole family were committed Zionists, as were most Eastern European/Russian Jews who were able to flood into the West because of the war. ‘Bea’ finally got her own papers to emigrate to Canada.
A Jewish organization, Sharit Ha-Platah, gathered names of Jews who were liberated from Dachau and it’s many sub-camps and published them in 1946. This is the only record so far found with the names of Hilda and Beatrice Wiesel, and it is a self-identified list of Jews by Jews, not an official German record of forced laborers or prisoners. So the hard evidence for the Wiesel family is not there. It doesn’t mean they weren’t, however; it’s just that we’re left with believing what they say, because we want to or because we’re expected to.
The easiest option is to go along with Elie Wiesel’s story that he was in those camps, and question his credibility from other angles, such as the in-credible stories he tells. This is what revisionists had done before Nikolaus Grüner came along and released documents he had obtained from Buchenwald and the correspondence he had with the archivists there. These documents cannot be ignored, in spite of what other nonsense Grüner writes in his book Stolen Identity. These documents have caused a sea change in revisionism about Elie Wiesel, to the extent that it can be divided between pre-Grüner and post-Grüner research and writing.
Wiesel needs to expose himself to questions
Because of these documents, it is up to Elie Wiesel to come forth and answer questions about them. But being that he is completely unprepared to do so, this job has been given to his surrogates—Professor Waltzer for one. Kenneth Waltzer promised, with a lot of bombast, that he would produce proof that Elie is Lazar and that Shlomo is Abraham, but for a year now he has failed to produce it, or even say anything more about it. He has also failed to come out with his promised book, “The Rescue of Children and Youths at Buchenwald,” which was to include Elie Wiesel. In the opinion of this writer, Waltzer is as big a fraud as Wiesel, selling emotion and sentimentality instead of factual history. They are both supported with professorships at well-funded universities.
So, back to the main question: Was Elie Wiesel in Auschwitz and Buchenwald? As I said, my answer is still no … and no one should accept that he was without some further explanation from him, during which he subjects himself to questions. If he’s genuine, he can certainly withstand questions. That, however, is not going to happen because … fill in your own answer.
Elie Wiesel has kept the details of his life before 1955 vague. He has managed to prevent unwanted questions from being asked of him. He hides behind a stated aversion to “holocaust deniers” so that anyone who is not a 100% believer is not welcome in his company. He gets away with the ‘moral outrage’ he professes toward anyone who doubts, thus no interviewer, reporter, writer, academic, student or even President dares to doubt in his presence. It works like a charm.
Endnotes
1. Danuta Czech, Auschwitz Chronicle: 1939-1945. New York: Henry Holt, 1997
2. APMO, D-Bu 3/17, pp. 18-85, 87 (transport list as cited by Czech in Auschwitz Chronicle)
3. Hilda was obviously unaware that the march itself was only 24 hours, probably because she had heard so many false and exaggerated stories about “endless days of marching” that proliferate in survivor stories.
4. Harry James Cargas, ed. Voices from the Holocaust, Lexington: University of Kentucky Press, 1993. pp. 116-22.
7 Comments
Category Featured | Tags: Tags: Auschwitz-Birkenau, Buchenwald, Elie Wiesel, Hilda Wiesel, Holocaust fraud, Miklos Grüner, Night, Shlomo Wiesel, Un di velt holt geshvign,
Social Networks: Facebook, Twitter, Google Bookmarks, del.icio.us, StumbleUpon, Digg, Reddit, Posterous.
Tuesday, February 7th, 2012
by Carolyn Yeager
As expected, a judge in a Budapest court has rejected a lawsuit brought by Hungarian-born Nikolaus (Miklós) Grüner against Chabad rabbi Slomo Köves for helping to arrange Elie Wiesel’s “Homecoming Tour” to Hungary in 2009. Grüner maintains that Elie Wiesel is not Hungarian and not a holocaust survivor.
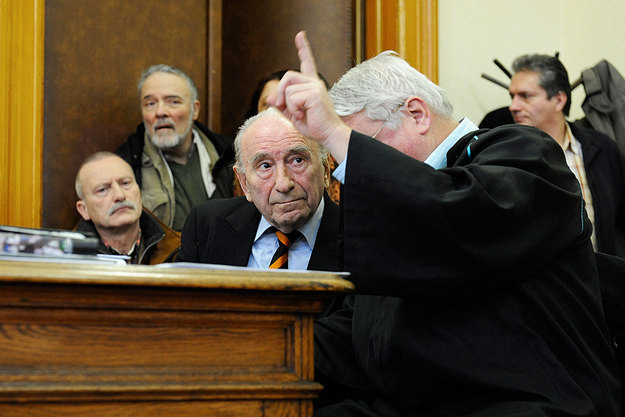 Nikolaus Grüner, center facing camera, watches as a barrister makes a point in court during his January 27th hearing.
Nikolaus Grüner, center facing camera, watches as a barrister makes a point in court during his January 27th hearing.

The lawsuit was brought against Köves, described as the rabbi of the Chabad community in Budapest, (pictured right) rather than Wiesel because of the lack of jurisdiction over an American citizen by a Hungarian court. Grüner’s personal dispute with Köves now seem to have taken precedence; he is complaining that “The rabbi basically called me a liar in his statement.”
According to Bos-News Life Christian news service, Gruner said he was angered by the court’s statement Monday, February 6 that it wasn’t able to rule on whether Wiesel had lied about his Holocaust past because he lives in America. “I never wanted the Hungarian court to rule on that issue. However I wanted the court to give an opinion about the unjustified statements made by the rabbi.”
The rabbi had called the 83-year-old Grüner “an elderly man with some kind of complex” and accused him of “falsifying history” by claiming Wiesel is not survivor of Auschwitz and Buchenwald. Köves also publicly likened Grüner to American author Norman Finkelstein, who wrote The Holocaust Industry. Finklestein is considered something of a “holocaust denier” by Jews even though he is simply critical of the way it has been marketed for immense profits to Israel.
Grüner says that these kind of remarks from Köves could undermine his plans to directly sue Wiesel in the United States; he wanted the court to rule against Köves for making these remarks. He told Bos-News Life that he would “appeal the ruling and court procedure and demand a new trial” later this month. The news service also reported that Grüner plans to travel to the United States this month to demand that American authorities extradite Wiesel to Hungary and to meet a lawyer representing Holocaust survivors.
This last appears to Elie Wiesel Cons the World to be a ‘mission impossible.’ However, we applaud Mr. Grüner for doing his best to keep the Elie Wiesel hoax issue alive in the public mind and wish him well.
2 Comments
Category Featured | Tags: Tags: Bos-News Life, Budapest, Elie Wiesel, Hungary, Miklos Grüner, Rabbi Köves,
Social Networks: Facebook, Twitter, Google Bookmarks, del.icio.us, StumbleUpon, Digg, Reddit, Posterous.
Saturday, September 11th, 2010
by Carolyn Yeager
copyright 2010 carolyn yeager
What can be simpler than to compare two signatures of the same name to determine whether they are indeed the same or two different individuals? Fortunately, we have available not only the signature of Elie Wiesel, but also that of Lázár Wiesel. The latter is on the “Military Government of Germany Concentration Camp Inmates Questionnaire.” This Questionnaire (Fragebogen in German) can be seen among The Documents pertaining to the Lazar Wiesel/Elie Wiesel question.
The importance of this lies in the fact that we only have one Lazar Wiesel at a time at Buchenwald, according to the records. Lazar Wiesel, born Sept. 4, 1913 arrived at the camp on January 26, 1945, along with his brother Abram, born Oct. 10, 1900, in a large transport from Auschwitz. They both have Buchenwald registration (or entry) numbers.
After the liberation in April, a questionnaire is filled out by a Lázár Wiesel who accents his name in the Hungarian style, giving a birth date of Oct. 4, 1928, and this Lazar is listed on the “childrens” transport to France in July. Neither of these Lazar Wiesel’s fit Elie Wiesel with his birth date of Sept. 30, 1928, and now I find his signature doesn’t match either.
On the left, Elie Wiesel’s well-known signature; on the right, the signature of Lázár Wiesel (last name is written first).
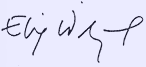
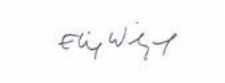 Two more examples of Elie’s book signing. The same style of open, very loose script is also found on the form he filled out for the Yad Vashem Central Database of Shoah Victims, testifying to his father Shlomo’s death at Buchenwald in January 1945. You can view it on their Internet site. Shlomo Vizel is on page 4 of the names.
Two more examples of Elie’s book signing. The same style of open, very loose script is also found on the form he filled out for the Yad Vashem Central Database of Shoah Victims, testifying to his father Shlomo’s death at Buchenwald in January 1945. You can view it on their Internet site. Shlomo Vizel is on page 4 of the names.
I suggest that this signature comparison leaves little doubt that the two men are not the same person. Elie Wiesel is NOT the Lázár Wiesel who was liberated from Buchenwald, or who traveled to France with the “Buchenwald Orphans.”1 The young Lázár Wiesel, born Oct. 4, 1928 according to these Buchenwald documents, and whose name and birth date appear on the transport list of “orphaned children” sent from Germany to France in July 1945 (see #14 on The Documents page) has such a visibly different style of writing from the Elie Wiesel who falsely claims to be on that list,2 that the two cannot be confused.
DATES OF ARREST DON’T MATCH
There is more evidence that they are not the same person in the form of the date of arrest shown on the same questionnaire. The date of arrest of Lázár Wiesel is given as April 16, 1944. That is the same day Samuel Jakobovits was arrested. Samuel and Lázár gave each others name as one of three references on their questionnaires, suggesting they were probably friends, or at least acquaintances, that had arrived at the same time.
Myklos Grüner’s date of arrest on his questionnaire is also 16 April 1944, from the city or surrounding area of Nyiregyhaza, Hungary. This can raise a question about the use of April 16 as some kind of “standard” date used by the military authorities in charge of the questionnaires. However, in his book Stolen Identity, Grüner does specify that on April 14, Hungarian gendarmes evacuated the entire population in the ghettos around the city of Nyiregyhaza, approximately 17,000 people. Six days later, “we too were driven from our homes” in Nyiregyhaza to a “holding area” leading to a railway track with a large loading platform, whereupon they boarded a “goods train.” Their destination was Auschwitz-Birkenau, where they would have arrived sometime between April 24 and April 30, 1944 (depending upon how long they stayed in the “holding area” before starting the 3 to 4-day journey).3
By contrast, we know by the authority of Elie Wiesel’s book Night that his family was not arrested on that date. In the “revised and updated” new translation of 2006, Wiesel gives his family’s date of deportation to the “small ghetto” as May 17, 1944. I arrive at this date because Wiesel writes that it was “some two weeks before Shavuot” (Shavuot fell on May 28 in 1944 4) that the deportation order was announced to his family and neighbors. [Remember, Sighet had 90,000 residents, at least one-third of them Jews, while Wiesel makes it sound like he lived in a little village.] Departures were to take place “street by street” starting the next day. That would be May 15. But the Wiesel family was scheduled to leave in the 3rd group, which left two days later, on May 17. After being marched to the “small ghetto,” they stayed there “a few days.” On a “Saturday,” they boarded trains.5 The 20th of May, 1944 was a Saturday
Thus, according to official concentration camp documents and Elie Wiesel’s own testimony, we can demonstrate that Lázár Wiesel was arrested approximately one full month prior to Elie Wiesel being arrested. Elie Wiesel is not the Lázár Wiesel of the Buchenwald documents.
Footnotes:
- Ken Waltzer will present on his book-in-progress, The Rescue of Children and Youth in Buchenwald, at James Madison College on April 11, 2007. In this book, Waltzer explores why, when the U.S. Third Army liberated Buchenwald, April 11, 1945, there were 904 children and youth still alive to be liberated. Among these were Elie Wiesel, a 16-year-old youth from Transylvania, (later Nobel Peace Prize winner) and also Israel Meir Lau, an 8-year-old child from Poland (later Israel Prize winner. http://www.jmc.msu.edu/faculty/show.asp?id=32
- It may be that Elie Wiesel has not made such claims himself, but they have been made by others to support the thesis that he is the one referred to. These others include Ken Waltzer, director of the Jewish Studies Program at Michigan State University, and the U.S. Holocaust Memorial Museum.
- Nikolaus Grüner, Stolen Identity, Stockholm, 2005-2006, pg. 18-19
- “On the second day of Shavuot, 1944 (29 May 1944)” http://www.shtetlinks.jewishgen.org/Vamospercs/
- Elie Wiesel, Night, Hill & Wang, New York, 2006, pg.12-21.
14 Comments
Category Featured | Tags: Tags: Buchenwald liberation, Miklos Grüner, military govt. questionaires, Night, Wiesel signatures,
Social Networks: Facebook, Twitter, Google Bookmarks, del.icio.us, StumbleUpon, Digg, Reddit, Posterous.
Sunday, September 5th, 2010
by Carolyn Yeager
copyright 2010 Carolyn Yeager
Part III: Nine reasons why Elie Wiesel cannot be the author of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign (And the World Remained Silent).
1. The only original source for the existence of an 862-page Yiddish manuscript is Elie Wiesel.
Wiesel’s 1995 memoir All Rivers Run to the Sea is the first time he mentions writing this book in the spring of 1954 on an ocean vessel on his way to Brazil.
In the original English translation of Night, Hill and Wang, 1960, there is no mention of the Yiddish book from whence it came. Nowhere does it name the original version and publication date. There is no preface from the author, only a Foreword by Francois Mauriac who was satisfied to simply call the book a “personal record.”
In his 1979 essay titled “An Interview Unlike Any Other,” Wiesel declares that his first book was written “at the insistence of the French Catholic writer Francois Mauriac” after their first meeting in May 1955. There is no mention in this essay of a Yiddish book, of any length. By “his first book” he obviously meant La Nuit, published in 1958 in France. 38
In his Nobel Peace Prize acceptance speech in Dec. 1986, Wiesel doesn’t mention his books, but refers twice to the “Kingdom of Night” that he lived through and once says, “the world did know and remained silent.” So it’s not like he was unaware of this book title. 39
Thus, All Rivers Run appears to be the first mention of the Yiddish origin of Night. Why did Elie Wiesel decide to finally write about And the World Remained Silent in that 1995 memoir? Could it have been because in 1986, after being formally awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in Stockholm, he was “reunited” with a fellow concentration camp inmate Myklos Grüner, who, after that meeting, read the book Night that Wiesel had given him, recognized the identity of his camp friend Lazar Wiesel in it, and from that moment began his investigation of who this man named Elie Wiesel really was?
Grüner writes in his book Stolen Identity, “My work of research to find Lazar Wiesel born on the 4th of September 1913 started first in 1987, to establish contact with the Archives of Buchenwald.” 40 He was also writing to politicians and newspapers in Sweden. This could not have failed to attract the notice of Elie Wiesel and his well-developed public relations network. Grüner tracked down Un di Velt Hot Gesvign as the original book from which Night was taken, and believed it was written by his friend Lazar Wiesel and “stolen” somehow by “Elie.”41
This could account for why Elie Wiesel suddenly began to speak and write about his Yiddish book, published in Buenos Aires, Argentina in 1956. (It was actually inserted into the larger Polish collection in late 1954, according to the Encyclopedia Judaica [see part II], and printed as a single book in 1955, with a 1956 publication date.) 42
Wiesel claims the 862-page typescript he handed over to publisher Mark Turkov on the ship docked at Buenos Aires in spring 1954 was never returned to him.43 (Wiesel had not made a copy for himself, and didn’t ask Turkov to make copies and send him one, according to what he wrote in All Rivers.)
The only other person reported to ever have had the typescript in his hands was Mr. Turkov, but there is no word from him about it. We can only say for sure that he published a 245-page volume in Polish Yiddish titled Un di Velt Hot Gesvign by Eliezer Wiesel. The book has no biographical or introductory material—only the author’s name. Eric Hunt has made this Yiddish book available on the Internet 44 and is seeking a reliable translator.
There is practically nothing written about Mark Turkov. [Added 1-13-25: Since then I have found this: https://congressforjewishculture.org/people/4108/Turkov-Mark-May-11-1904-April-29-1983 in English, with some interesting images -cy] You can read about his accomplished family [there] and here. He was born in 1904 and died 1983. There is no direct testimony from Mark Turkov, that I have been able to find, that he ever received such a manuscript. Since Turkov lived until 1983 to see the book Night become a world-wide best seller, I find this inexplicable. Did no one seek him out to ask him questions, ask for interviews, take his picture? But at the same time, that becomes understandable if Night was not connected with Un di Velt until after 1986 [after Turkov’s death -cy], when Miklos Grüner entered the picture and began asking questions.
We’re left with asking: was there ever an 862 page manuscript? And if not, why does Wiesel say he wrote that many pages?
2. Wiesel could not have written the 862 pages in the time he says he did.
According to what he writes in All Rivers, Wiesel’s voyage lasted at most two weeks. Spending all his time in his cabin, cut off from all sources of information, seemingly on the spur of the moment (not pre-planned), he types feverishly and continuously on a portable typewriter (even though he’s written all his other books in long-hand, by his own testimony) and produces 862 typewritten pages without re-reading a single one. That comes out to an average of almost 62 pages daily, for 14 days straight. Is there anyone who could accomplish such a feat?
The scrawny Elie Wiesel is not a superman; he is not even the intense type, but more of a spaced-out thoughtful type. What’s more, he was not even tired out by this marathon effort, but immediately upon the ship docking at Sao Paulo, he became the active spokesman for a group of “homeless” Jews.
Here is a picture of a Yiddish typewriter from the 1950’s. Notice the red/black ribbon in front of the roller where the paper is inserted.
 A point to consider about the typewriter: He would have used up a lot of ribbons typing that many pages. Ribbons are those inked strips of fabric that the metal characters hit to make the black or color impression on the white paper. This is something the computer generation doesn’t know anything about. The ribbons did not last all that long; the characters on the page got lighter as the ribbon was hit again and again; thus he would have been installing a new one with some regularity. As I recall, replacing the ribbon was not a very fun thing to do. Did he plan on writing day and night, and bring plenty of ribbons with him? Was he able to purchase more ribbons for his particular machine in Brazil?
A point to consider about the typewriter: He would have used up a lot of ribbons typing that many pages. Ribbons are those inked strips of fabric that the metal characters hit to make the black or color impression on the white paper. This is something the computer generation doesn’t know anything about. The ribbons did not last all that long; the characters on the page got lighter as the ribbon was hit again and again; thus he would have been installing a new one with some regularity. As I recall, replacing the ribbon was not a very fun thing to do. Did he plan on writing day and night, and bring plenty of ribbons with him? Was he able to purchase more ribbons for his particular machine in Brazil?
Another point about the typewriter brought up earlier by a reader: Was Wiesel a fast or slow typist? Many journalists were, and are, two-fingered (hunt and peck) typists because they never took typing classes. Where would Elie Wiesel have learned to type? In the newspaper office? If he was not a full-finger typist, it’s even less likely he could have churned out all those pages. Not to mention that these old typewriters did not allow the ease, and therefore speed, of our modern [computer] keyboard. These are practical questions that help us to ground ourselves in reality.
In addition, this manuscript is said to have been written in the style of a detailed history of the entire process of deportation, detention, people and places, punishments, liberation, yet Wiesel has no reference materials on board ship—only his memory. And since it was nine years since the events had ended, certainly some dulling of his memory had occurred. This simply could not be accomplished in the kind of mad rush Wiesel describes in All Rivers.
3. Wiesel’s motivation for attempting to write his concentration camp memories when he did is not given and is not apparent.
It’s astonishing that Wiesel gives only one paragraph in his memoir to the entire process of writing this book. He doesn’t write of thinking about it ahead of time. In fact, just at the time of his trip to Brazil he is carrying on a love affair in Paris, as well as being very busy, enthused and ambitious about his journalist assignments. Hanna, his love interest, had proposed marriage to him and he records in All Rivers that it “haunted me during the crossing,” during which time he “was worried sick that I might be making the greatest mistake of my life.”45 Yet, as though a kind of afterthought, he then tells us he spent the entire crossing holed up in his cabin, feverishly writing his very emotionally traumatic “witness” to the holocaust, even though only 9 years of his self-imposed 10-year vow of silence had passed.
In over 100 pages prior to the trip, Wiesel does not mention wanting to write about or even reflecting on his concentration camp year. The only explanation he includes in that paragraph is: “My vow of silence would soon be fulfilled; next year would mark the tenth anniversary of my liberation.”46 Then, just as suddenly, when he steps on land in Brazil, he is fully engaged in journalism and Hanna once again. He has given the typescript away and seems to have totally forgotten about it.
4. Wiesel had no opportunity to edit the 862 pages of And the World Remained Silent to the 245-page published version, yet he says he did.
Wiesel writes in All Rivers, “I had cut down the original manuscript from 862 pages to the 245 of the published Yiddish edition. French publisher Jerome Lindon edited La Nuit down to 178.”47 The time is 1957 and Wiesel is pleased a French publisher has been found for the manuscript he gave to Francois Mauriac—his French translation of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign, of which Wiesel says of the latter, “I had already pruned and abridged considerably.” The publisher, Lindon, now “proposed new cuts throughout, leading to significant differences in length among the successive versions.”
He repeats something similar in his Preface to the new 2006 translation of Night:
Though I made numerous cuts, the original Yiddish version still was long.48
He can only mean the 245-page book as the “original Yiddish version”—thus he “made cuts” from the longer version. But Wiesel could not have done it because he never saw the manuscript again after he supposedly gave it to Mark Turkov. He writes of his extremely busy life following the Brazil trip—covering world events as a journalist, spending time in Israel again before considering moving to NYC. He sounds underwhelmed when he reports receiving a copy of the Yiddish book in the mail from Turkov in Dec.1955, and devotes only a couple sentences to it. 49
Another time he refers to reducing the 245-page Yiddish version into a French version. Speaking of Mauriac:
He was the first person to read Night after I reworked it from the original Yiddish. 50
It is just these kinds of comments that cause the confusion remarked upon by Naomi Siedman in her essay commenting on Jewish rage in Wiesel’s first book. She writes that certain “scholars,” such as Ellen Fine and David Roskies give conflicting reports on the length of Wiesel’s original book, and it’s not clear just which book they are talking about. In my opinion, the reason for all the confusion is that they take Wiesel at his word as an honest witness … perhaps with some memory lapses. They won’t entertain the idea that this is part of a cover-up, the details of which Mr. Wiesel has a hard time keeping straight.
5. Wiesel’s recognized “style” and the style of the Yiddish book are noticeably different.
Not enough is known as yet to non-Yiddish readers like me about the content of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign to make the strongest case for the above statement, but a Jewish critic has provided some passages from the Yiddish book and I will quote from her (except for one passage from Joachim Neander). Naomi Siedman, in her long essay cited above, says this:
For the Yiddish reader, Eliezer Wiesel’s memoir was one among many, valuable for its contributing an account of what was certainly an unusual circumstance among East European Jews: their ignorance, as late as the spring of 1944, of the scale and nature of the Germans’ genocidal intentions. 51
In other words, holocaust narratives had already developed a “Yiddish genre” and the Wiesel memoir fit in with them. She explains:
When Un di velt had been published in 1956, it was volume 117 of Turkov’s series, which included more than a few Holocaust memoirs. The first pages of the Yiddish book provide a list of previous volumes (a remarkable number of them marked “Sold out”), and the book concludes with an advertisement/review for volumes 95-96 of the series, Jonas Turkov’s Extinguished Stars. In praising this memoir, the reviewer implicitly provides us with a glimpse of the conventions of the growing genre of Yiddish Holocaust memoir. Among the virtues of Turkov’s work, the reviewer writes, is its comprehensiveness, the thoroughness of its documentation not only of the genocide but also, of its victims.
[…]
Thus, whereas the first page of Night succinctly and picturesquely describes Sighet as “that little town in Transylvania where I spent my childhood,” Un di Velt introduces Sighet as “the most important city [shtot] and the one with the largest Jewish population in the province of Marmarosh,” and also “Until, the First World War, Sighet belonged to Austro-Hungary. Then it became part of Romania. In 1940, Hungary acquired it again.” 52
The Yiddish book has a different “feel” to it from Night; not only a different style, but a different personality is behind it. Ms. Seidman told E.J. Kessler, editor of The Forward:
The two stories can be reconciled in strict terms,” she said, “but they still give two totally different impressions, one of a person who’s desperate to speak versus one who’s reluctant.53
Here is a translation by Dr. Joachim Neander of a key passage in the Yiddish book, which he posted on the CODOH forum. It reveals an informal, talkative style, totally different from the spare, literary style used by Wiesel in all his books, even though the storyline is basically the same. Wiesel says he edited this book to its published form, but it doesn’t sound like him.
On January 15, my right foot began to swell. Probably from the cold. I felt horrible pain. I could not walk a few steps. I went to the hospital. The doctor examined the swollen foot and said: It must be operated. If you will wait longer, he said, your toes will have to be cut off and then the whole foot will have to be amputated. That was all I needed! Even in normal times, I was afraid of surgery. Because of the blood. Because of bodily pain. And now – under these circumstances! Indeed, we had really great doctors in the camp. The most famous specialists from Europe. But the means they had to their disposition were poor, miserable. The Germans were not interested in curing sick prisoners. Just the opposite.
If it had been dependent on me, I would not have agreed to the operation. I would have liked to wait. But it did not depend on me. I was not asked at all. The doctor decided to operate, and that was it. The choice was in his hands, not in mine. I really felt a little bit of joy in my heart that he had decided upon me.54
Back to Siedman’s translations. Two examples will have to suffice, from the Dedication and the very last paragraphs.
… while the French memoir is dedicated “in memory of my parents and of my little sister, Tsipora,” the Yiddish names both victims and perpetrators: “This book is dedicated to the eternal memory of my mother Sarah, father Shlomo, and my little sister Tsipora — who were killed by the German murderers.” 55
Now the book’s ending in the Yiddish version:
Three days after liberation I became very ill; food-poisoning. They took me to the hospital and the doctors said that I was gone. For two weeks I lay in the hospital between life and death. My situation grew worse from day to day.
One fine day I got up — with the last of my energy — and went over to the mirror that was hanging on the wall. I wanted to see myself. I had not seen myself since the ghetto. From the mirror a skeleton gazed out. Skin and bones. I saw the image of myself after my death. It was at that instant that the will to live was awakened. Without knowing why, I raised a balled-up fist and smashed the mirror, breaking the image that lived within it. And then — I fainted. From that moment on my health began to improve. I stayed in bed for a few more days, in the course of which I wrote the outline of the book you are holding in your hand, dear reader.
But — Now, ten years after Buchenwald, I see that the world is forgetting. Germany is a sovereign state, the German army has been reborn. The bestial sadist of Buchenwald, Ilsa Koch, is happily raising her children. War criminals stroll in the streets of Hamburg and Munich. The past has been erased. Forgotten. Germans and anti-Semites persuade the world that the story of the six million Jewish martyrs is a fantasy, and the naive world will probably believe them, if not today, then tomorrow or the next day.
So I thought it would be a good idea to publish a book based on the notes I wrote in Buchenwald. I am not so naive to believe that this book will change history or shake people’s beliefs. Books no longer have the power they once had. Those who were silent yesterday will also be silent tomorrow. I often ask myself, now, ten years after Buchenwald: Was it worth breaking that mirror? Was it worth it? 56
In contrast, Night ends with the gaze into the mirror at the very beginning of this passage. If the smashing of the mirror and the renewed will to live he felt from it was Elie Wiesel’s own experience, why would he leave it out in La Nuit? Because the publisher wanted it out? Not at all likely. Mauriac? Doubtful. It’s much more likely that it was not Elie Wiesel’s experience and it was not the kind of story he felt he could or wanted to tell.
Also note that the Yiddish writer says he wrote the outline of the book while still in the Buchenwald hospital, and that the published book is based on those notes. Elie Wiesel has never suggested that he began any writing in Buchenwald.
6. Wiesel wrote only one book in Yiddish; all subsequent books are in French.
If we could ask Elie Wiesel why he wrote his concentration camp memoirs in Yiddish, when he was already fluent and writing in French, we would probably get the answer he gave to his friend Jack Kolbert, who was writing a book about him:
“I wrote my first book, Night, in Yiddish, a tribute to the language of those communities that were killed. I began writing it in 1955. I felt I needed ten years to collect words and the silence in them.” 57
Alright. But we should also ask, just how good was Wiesel’s written Yiddish, that he could write this “enormous tome” in such a short time? After Nov. 29, 1947, Wiesel sought out and was given a job with the Irgun Yiddish weekly in Paris called Zion in Kamf. He tells how he was put to work translating Hebrew into Yiddish.
The task was far from easy. I read Hebrew well and spoke fluent Yiddish, but my Germanized written Yiddish wasn’t good. My style was dry and lifeless, and the meaning seemed to wander off into byways lined with dead trees. That was not surprising, since I was wholly ignorant of Yiddish grammar and its vast, rich literature.58
Even though he continued to translate and eventually write for the paper, he also spoke and wrote otherwise in French. He was attending classes at the Sorbonne and reading French classics and the newer existentialists. Following this first and only Yiddish book, Wiesel has done all his writing in French, by his own account—and in longhand, while the Yiddish was written on a typewriter.
It’s hard to reconcile Wiesel’s professed love of Yiddish 59 with his failure to do any writing beyond Un di Velt in that language. It’s suggested it is because Yiddish readers are a diminishing breed. No doubt, but that was already the case in 1954. For what it’s worth, Myklos Gruner records that when he met Elie Wiesel at their pre-arranged encounter in Stockholm in 1986, he asked Elie if he would like to speak in “Jewish,” and Elie said “no.” They ended up speaking together in English.60 Wiesel seems to have no interest in keeping the language alive.
7. Wiesel gives contradictory dates for the writing of his first book, and is fuzzy about what his “first book” is.
Wiesel makes it definite in All Rivers that he wrote the Yiddish book in the spring of 1954, in a cabin of a ship going to Brazil. But around the year 2000 he tells his friend Jack Kolbert:
It took me 10 years before I felt I was ready to do it. I wrote my first book, Night, in Yiddish, a tribute to the language of those communities that were killed. I began writing it in 1955. I felt I needed ten years to collect words and the silence in them. 61
So, is it 1954 or 1955? Wiesel says in All Rivers he met Francois Mauriac in May 1955, one year after his Brazil trip. Mauriac is often credited as the one who convinced Wiesel to end his silence, which culminated in Night. In his 1979 essay, “An Interview Unlike Any Other,” Wiesel writes:
Ten years of preparation, ten years of silence. It was thanks to Francois Mauriac that, released from my oath, I could begin to tell my story aloud. I owe him much, as do many other writers whose early efforts he encouraged. But in my case, something totally different and far more essential than literary encouragement was involved. That I should say what I had to say, that my voice be heard, was as important to him as it was to me.
[…]
(H)e urged me to write, in a display of trust that may have been meant to prove that it is sometimes given to men with nothing in common, not even suffering, to transcend themselves.62
He also wrote, in the same essay on the next page (17):
Paris 1954. As correspondent for the Israeli newspaper Yedioth Ahronoth, I was trying to move heaven and earth to obtain an interview with Pierre Mendes-France, who had just won his wager by ending the Indochina war. Unfortunately, he rarely granted interviews, choosing instead to reach the public with regular talks on the radio. Ignoring my explanations, my employer in Tel Aviv was bombarding me with progressively more insistent cabled reminders, forcing me to persevere, hoping for a miracle, but without much conviction. One day I had an idea. Knowing the admiration the Jewish Prime Minister bore the illustrious Catholic member of the Academie, why not ask the one to introduce me to the other? The occasion presented itself. I attended a reception at the Israeli Embassy. Francois Mauriac was there. Overcoming my almost pathological shyness, I approached him, and in the professional tone of a reporter, requested an interview. It was granted graciously and at once.
Wiesel continues the confusion around ’54 and ’55 when interviewed by the American Academy of Achievement on June 29, 1996 in Sun Valley, Idaho.63 In answer to the question “What persuaded you to break that silence?” he replied:
Oh, I knew ten years later I would do something. I had to tell the story. I was a young journalist in Paris. I wanted to meet the Prime Minister of France for my paper. He was, then, a Jew called Mendès-France. But he didn’t offer to see me. I had heard that the French author François Mauriac […] was his teacher. So I would go to Mauriac, the writer, and I would ask him to introduce me to Mendès-France. […]
Pierre Mendes-France became Prime Minister on June 18, 1954; his hold on that office ended on Jan. 20, 1955. Wiesel, according to his autobiography, had returned from Brazil, after writing and giving his 862-page Yiddish manuscript to Mark Turkov, expressly to cover the inauguration of France’s new Prime Minister for his Israeli newspaper.64 In this case, Wiesel’s first meeting with Mauriac had to be some time after mid-June 1954, since Mendes-France is already Prime Minister; it couldn’t have been in May or June 1955 because Mendes-France was long out of office. But in All Rivers, he puts his first Mauriac meeting in May 1955: “I first saw Mauriac in 1955 during an Independence Day celebration at the Israeli embassy.”(p.258) Israel’s Independence Day is May 14. Wiesel says the interview with Mauriac he obtained from that meeting resulted in his writing La Nuit and sending it to Mauriac one year later, in 1956. He continues describing that meeting to the Academy interviewer:
I closed my notebook and went to the elevator. He (Mauriac) ran after me. He pulled me back; he sat down in his chair, and I in mine, and he began weeping. […] And then, at the end, without saying anything, he simply said, “You know, maybe you should talk about it.”
He took me to the elevator and embraced me. And that year, the tenth year, I began writing my narrative. After it was translated from Yiddish into French, I sent it to him.
Wiesel says “the tenth year,” which would be 1955, but in the earlier part of the interview he is referring to 1954—because of Mendes-France. Snce he is mixing up the date, it’s no wonder we find the same mis-dating in stories about Wiesel’s life and accomplishments in books and on the Internet, including on Wikipedia pages.
Whenever it was that Wiesel had that fateful visit with Mauriac, he clearly did not mention that he had already written a very long Yiddish memoir, whether a year or a couple of months earlier. But had he written anything yet? Mauriac never alludes to a first Yiddish text. And as stated before, Wiesel himself didn’t either, until his 1995 memoir All Rivers Run to the Sea. This is truly noteworthy. Also, the title Un di Velt Hot Gesvign or, in English, And the World Remained Silent does not appear on the long list of “books by Elie Wiesel” at the beginning of All Rivers or the 2006 translation of Night.
To clarify an important problem Wiesel faces here: Wiesel, prior to 1990, claims to have first met and interviewed Mauriac in the spring of 1954 after returning from Brazil, but later changed it to May or June 1955. But even after that, he sometimes reverted to the 1954 scenario. When you are inventing all or parts of your life story, it’s difficult to keep it straight, especially when your guard is down.
A likely reason is his need to fit the writing and publication of the Yiddish book into his “schedule”, something he had not considered, or just ignored, previous to the Yiddish book being brought to the attention of the world by Myklos Grüner .


8. There are striking differences between Night, his “true story” derived from the Yiddish book, and his autobiography All Rivers Run to the Sea.
If Night is a true account of Wiesel’s holocaust experience, how to explain such major differences in the key passages that are compared below. In the first book it is his foot, in the latter his knee that is operated on right before the 1945 evacuation of Auschwitz.
Toward the middle of January, my right foot began to swell because of the cold. I was unable to put it on the ground. I went to have it examined. The doctor, a great Jewish doctor, a prisoner like ourselves, was quite definite: I must have an operation! If we waited, the toes—and perhaps the whole leg—would have to be amputated. .65
[…]
The doctor came to tell me that the operation would be the next day […] The operation lasted an hour.66
The doctor told him he would stay in the hospital for two weeks, until he was completely recovered. The sole of his foot had been full of pus; they just had to open the swelling. But, two days after his operation there was a rumor going round the camp that the Red Army was advancing on Buna. Not able to decide whether to stay in the hospital or join the evacuation, he left to look for his father.
“My wound was open and bleeding; the snow had grown red where I had trodden.” That night his “foot felt as if it were burning.” In the morning, he “tore up a blanket and wrapped my wounded foot in it.” 67
He and his father decided to leave. That night they marched out. They were forced to run much of the night and he ran on that foot, causing great pain. But after that he doesn’t mention it again. By contrast, in All Rivers, it is not his foot, but his knee that is operated on!
January 1945. Every January carried me back to that one. I was sick. My knee was swollen, and the pain turned my gait into a limp. […] That evening before roll call, I went to the KB. My father waited for me outside […] At last my turn came. A doctor glanced at my knee, touched it. I stifled a scream. “You need an operation,” he said. “Immediately.” […] One of the doctors, a tall, kind-looking man, tried to comfort me. “It won’t hurt, or not much anyway. Don’t worry, my boy, you’ll live.” He talked to me before the operation, and I heard him again when I woke up.” 68
[…]
January 18, 1945. The Red Army is a few kilometers from Auschwitz. […] My father came to see me in the hospital. I told him the patients would be allowed to stay in the KB […] and he could stay with me […] but, finally, we decided to leave with the others, especially since most of the doctors were being evacuated too.69
No further mention of the knee. How can we account for this bizarre change from foot to knee? It seems that as weak as Wiesel presents himself to be at Buna, he could not himself believe that he could run around on a foot that had just been operated on for pus in the sole, with no protection. So he simply changed it to his knee.
The next passage is after the liberation of Buchenwald on April 11, 1945. In Night:
Our first act as free men was to throw ourselves onto the provisions. We thought only of that. Not of revenge, not of our families. Nothing but bread.
And even when we were no longer hungry, there was still no one who thought of revenge. On the following day, some of the young men went to Weimar to get some potatoes and clothes—and to sleep with girls. But of revenge, not a sign.
Three days after the liberation of Buchenwald I became very ill with food poisoning. I was transferred to the hospital and spent two weeks between life and death.70
In All Rivers, Wiesel changes the story. He writes:
A soldier threw us some cans of food. I caught one and opened it. It was lard, but I didn’t know that.71 Unbearably hungry—I had not eaten since April 5—I stared at the can and was about to taste its contents, but just as my tongue touched it I lost consciousness.
I spent several days in the hospital (the former SS hospital) in a semiconscious state. When I was discharged, I felt drained. It took all my mental resources to figure out where I was. I knew my father was dead. My mother was probably dead ….. 72
From two weeks to only several days spent in the hospital. Could this change have anything to do with the famous “Buchenwald survivor” photograph73 that Elie discovered himself in sometime after 1980, when he was actively seeking a Nobel Prize? If he were in the hospital “between life and death” for two weeks following April 14 or so, he could not be in that photograph taken on April 16. The author of And the World Remained Silent, whoever he is, never claimed to be in that photograph.
9. Elie Wiesel refuses to back up his authorship by showing his tattoo.
If Elie Wiesel is the man who wrote Un di Velt Hot Gesvign, the source of the world-famous Night—the same man who wrote about receiving the tattoo number A7713 at Auschwitz in 1944—why won’t he show us this tattoo on his arm? And why do we see video of his left forearm with no tattoo visible at all? Wiesel could so easily clear up this problem, but he doesn’t choose to do so.
Endnotes:
38) Elie Wiesel, A Jew Today, Vintage Books, 1979, 260 pg.
39) http://worldsgreatestenglishclass.com/media/ww2/19EWSpeech.pdf
40) Stolen Identity, p. 50
41) Ibid, p. 43. Grüner mentions the 862 pages twice, but not with proof of their existence. “… Lazar Wiesel’s manuscript […] tell us his story and covers his survival of the Holocaust in 862 pages.” Also, “… had to use Lazar’s false identity in Paris and his existing manuscript of 862 pages …”
42) All Rivers, p. 277. “In December (1955) I received from Buenos Aires the first copy of my Yiddish testimony And the World Stayed Silent,” which I had finished on the boat to Brazil.”
43) Ibid.
44) http://rapidshare.com/files/441835370/Elie-Wiesel-Night-Yiddish.pdf
45) All Rivers, p. 239
46) Ibid, p. 240
47) Ibid, p. 319
48) Night, p. x
49) All Rivers, p. 277
50) Ibid. p. 267
51) Siedman, “Jewish Rage”
52) Ibid.
53) “The Rage that Elie Wiesel Edited Out of Night,” E.J. Kessler, ‘The Forward‘, October 4, 1996
54) http://forum.codoh.com/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=6146
55) Siedman, “Jewish Rage,” (trans. from Un di Velt)
56) Ibid. (Un di Velt, 244-45)
57) Jack Kolbert, The Worlds of Elie Wiesel: An Overview of His Career and His Major Themes, Susquehanna University Press, Selinsgrove, PA, 2001, p. 29
58) All Rivers, p.163
59) Ibid. p.291-92
60) Stolen Identity, p.31
61) Kolbert, p. 29
62) “An Interview Unlike Any Other,” Elie Wiesel, A Jew Today, trans. Marion Wiesel (New York, 1979), p.16
63) http://www.achievement.org/autodoc/page/wie0int-3
64) All Rivers, p. 242: “I had been away for two months when Dov recalled me to Paris to cover Pierre Mendes-France’s accession to power. I flew back …” This had to be in June 1954.
65) Night, p.82
66) Ibid. p.83
67) Ibid. p.87
68) All Rivers, p.89-90
69) Ibid. p.91
70) Night, p.115-16
71) Why would soldiers throw cans of lard? Sounds terribly disorganized and irregular. How did he open the can? If he didn’t know it was lard, and lost consciousness before he tasted it, we must assume someone in the hospital told him after he regained consciousness that he had been holding a can of lard when he was brought in. Either that or it’s just made up.
72) All Rivers, p.97
73) http://www.eliewieseltattoo.com/buchenwald
8 Comments
Category Featured | Tags: Tags: All Rivers Run to the Sea, Brazil, Buchenwald liberation, Francois Mauriac, knee/foot operation, Mark Turkov, Mendes-France, Miklos Grüner, Naomi Siedman, Night, Yedioth Ahronoth, Yiddish typewriter,
Social Networks: Facebook, Twitter, Google Bookmarks, del.icio.us, StumbleUpon, Digg, Reddit, Posterous.
Friday, August 20th, 2010
By Carolyn Yeager
copyright 2010 Carolyn Yeager
Part Two: Can the books Night and And the World Remained Silent have been written by the same author? What one critic reveals.
We know a lot about the man who calls himself Elie Wiesel from his own mouth and pen, but we know of the Lazar Wiesel born on Sept. 4, 1913 only through Miklos Grüner’s testimony, and of the author of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign (And the World Remained Silent) through the work itself. So let’s consider what we know of these two men before we look at their books.
The city of Sighet can be seen in the purple-colored Maramures district on this map of Greater Romania in the 1930’s.
Who is Elie Wiesel?
Elie Wiesel says in Night that he grew up in a “little town in Translyvania,” and his father was a well-known, respected figure within the Hasidic Orthodox Jewish community. However, Sanford Sternlicht tells us that Maramurossziget, Romania had a population of ninety thousand people, of whom over one-third were Jewish.15 Some say it was almost half. Sternlicht also writes that in April 1944, fifteen thousand Jews from Sighet and eighteen thousand more from outlying villages were deported. How many with the name of Wiesel might have been among that large group? I counted 19 Eliezer or Lazar Wiesel’s or Visel’s from the Maramures District of Romania listed as Shoah Victims on the Yad Vashem Central Database. Just think—according to their friends and relatives, nineteen men of the same name from this district perished in the camps in that one year. It causes one to wonder how many Lazar and Eliezer Wiesels didn’t perish, but became survivors and went on to write books, perhaps.
Lazare, Lazar, and Eliezer are the same name. Another variation is Leizer (prounounced Loizer). A pet version of the name is Liczu; a shortened version is Elie.16 In spite of having a popular, oft-used name, Elie Wiesel describes a unique picture of his life. The common language of the Orthodox Hasidic Jews of Sighet was Yiddish. Wiesel has said he thinks in Yiddish, but speaks and writes in French.17
In his memoir, he admits that he was a difficult, complaining child—a weak child who didn’t eat enough and liked to stay in bed.18 He comes across as definitely spoiled, the only son among three daughters.
According to Gary Henry, as well as other of Wiesel’s biographers and Wiesel himself, young Elie Wiesel was exceptionally fervent about the Hasidic way of life. He studied Torah, Talmud and Kabbalah; prayed and fasted and longed to penetrate the secrets of Jewish mysticism to such an extreme that he had “little time for the usual joys of childhood and became chronically weak and sickly from his habitual fasting.”19 His parents had to insist he combine secular studies with his Talmudic and Kabbalistic devotion. Wiesel says in Night that he ran to the synagogue every evening to pray and “weep” and met with a local Kabbalist teacher daily (Moishe the Beadle), in spite of his father’s disapproved on the grounds Elie was too young for such knowledge.
Of his elementary school studies, Wiesel writes: “[My teachers] were kind enough to look the other way when I was absent, which was often, since I was less concerned with secular studies than with holy books.” 20 And “in high school I continued to learn, only to forget.”
But his plans to become a pious, learned Jew came to an end with the deportation of Hungary’s Jews to Auschwitz-Birkenau. Wiesel has told this story both in his first book Night and in his memoir All Rivers Run to the Sea, and in many talks and lectures.
After liberation, in France, Wiesel met a Jewish scholar and master of the Talmud who gave his name simply as Shushani or Chouchani.21,22 In his memoir, Wiesel wrote:
It was in 1947 that Shushani, the mysterious Talmudic scholar, reappeared in my life. For two or three years he taught me unforgettable lessons about the limits of language and reason, about the behavior of sages and madmen, about the obscure paths of thought as it wends its way across centuries and cultures.23
Wiesel describes this person as “dirty,” “hairy,” and “ugly,” a “vagabond” who accosted him in 1947 when he was 18, and then became his mentor and one of his most influential teachers. Reportedly, when Chouchani died in 1968, Wiesel paid for his gravestone located in Montevideo, Uruguay, on which he had inscribed: “The wise Rabbi Chouchani of blessed memory. His birth and his life are sealed in enigma.” According to Wikipedia, Chouchani taught in Paris between the years of 1947 and 1952. He disappeared for a while after that, evidently spent some time in the newly-formed state of Israel, returned to Paris briefly, and then left for South America where he lived until his death.24
This could be important because it links up with Wiesel’s visits to Israel and his trip to Brazil in 1954. While the common narrative of Elie Wiesel’s post-liberation years focuses on his being a student at the Sorbonne University, Paris and an aspiring journalist, these sources reveal that he was still deeply into Jewish mysticism and involved with the Israeli resistance movement in Palestine.
Wiesel received a $16-a week-stipend from the welfare agencies.25 In addition, he worked as a translator for the militant Yiddish weekly Zion in Kamf. In 1948, at the age of 19, he went to Israel as a war correspondent for the French-Jewish newspaper L’arche, where he eventually became a correspondent for the Tel Aviv newspaper Yedioth Ahronoth.26 Shira Schoenberg at the Jewish Virtual Library puts it this way: “he became involved with the Irgun, a Jewish militant (terrorist) organization in Palestine, and translated materials from Hebrew to Yiddish for the Irgun’s newspaper […] in the 1950s he traveled around the world as a reporter.”27
The above paints a picture of a religiously-inclined personality, strongly drawn to, perhaps even obsessed with, the most mystical teachings and “secrets” of his Judaic tribe. By the age of 15, this trait was well-established. One year in detention of whatever kind (yet to be established for certain), hiding out, or other privations had no power to change these strong interests, which asserted themselves again immediately upon his “release.”
What kind of personality was Lazar Wiesel?
We only know of the Lazar Wiesel who was born on Sept. 4, 1913 through Miklos Grüner , and of the author of Un di Velt Hot Gesvign through the work itself. Note that I’m not claiming these two are one and the same.
Grüner writes in Stolen Identity28 that after the death of his father in Birkenau “after six months,” which must have been in October or early November 1944, he
went to see the friends of my father and brother, Abraham Wiesel and his brother Lazar Wiesel from Maramorossziget, [ …] Abraham was born in 1900 and his tattooed number was A-7712 and Lazar was born in 1913 and was tattooed as A-7713, whereas my father had A-11102, my brother A-11103, and I who stood after my brother finished up with the number A-11104. When they had heard the story of my father, they promised to take care of me and from then on, they became my protectors and brothers and an additional refuge …” (p. 24)
[…]
About three months had passed by, in my stage of hopelessness, I was informed by my “brothers” (Abraham and Lazar) that the Russians had managed to break through and they were on their way to liberate us from “BUNA,” Auschwitz III. (p. 25)
[…]
During the long march […] the walking became difficult and it was also hard to keep up with Abraham and Lazar. That was until I reached a place 30 km from Monowitz “Buna” called Mikolow, with a huge brickyard. Tired as I was after walking under the heavy winter conditions, I fell asleep on a pallet […] When night turned to dawn, I took my time and made my attempt to find Abraham and Lazar […] Later on I managed to find them and for the next 30 kilometres I had no problem in keeping up with them […] up to the next labor camp in Gliwice. After about three days stay in Gliwice, we were ordered to climb up onto an open railway carriage, without any given destination. […] Once again I lost Lazar and Abraham, but […] I found my old friend Karl … (p. 26)
The journey lasted about four days. On our arrival … I wobbled away to search for Abraham and Lazar. After a while, I found Lazar who told me that Abraham was having a hard time of it and he was not sure that Abraham would be able to pull through. He also mentioned that no matter what, he was going to stay with Abraham and was asking for God’s blessing. (p. 27)
[…]
When finally we were given our clothes (after showers, etc), we were registered and received new numbers that we had to memorize like children, and then we were assigned to Barrack 66. (Comment: “we” does not include Lazar and Abraham. Barrack 66 was the children’s barracks in the “small camp” at Buchenwald. Grüner was 16 yrs. old and his father had died.)
About a week later, I couldn’t believe my own eyes to see Lazar in our Block 66. He told me that Abraham had passed away four days after our arrival at Buchenwald. He made it clear that he had received special permission to join us children in Block 66, since he was so much older than us.
Five days before the liberation in April […] In our Block 66, attempts were made to get us to the main gate. The supervisor of our block, called Gustav with his red hair, indeed had managed to drive us out of the block and was determined to drive us to the gate. When we reached the middle of the yard, I pulled my trousers down (halfway), then ran off to the side and kept on running as fast as I could to the nearest block, which I believe was Block 57. I asked the man in the lower bunk if the place next to him was occupied, and I simultaneously took my position in the left hand corner of the bunk, where I remained until I was liberated.
If my memory serves me correctly, on the fourth day after my liberation, AMERICAN SOLDIERS came into the block and a picture was taken of us survivors of the Holocaust. […] This picture has become famous all over the world as a memory of the Holocaust.29 After a change of clothing and a medical examination, I went to look for Lazar, but unfortunately I could not find him anywhere. (p 28)

On page 30, Grüner writes: “When the liberating American soldiers came into our barrack, they discovered a block full of emaciated people lying in bunks. In the next minute a flashlight from a camera went off, and I without my knowing, was caught on the picture forever.”
Grüner never saw Lazar Wiesel again, since, according to him, Lazar was sent to France, and Grüner to a sanatorium in Switzerland. When Grüner was contacted in 1986 about meeting the Nobel Prize winner Elie Wiesel, he thought he was going to be meeting his old friend Lazar Wiesel.
What does Un di Velt Hot Gesvign tell us about Eliezer Wiesel?
Naomi Siedman, Professor of Jewish Culture at Graduate Theological Union, is one of the few academics to delve into Wiesel’s early writings with a critical spirit. Her very controversial essay “Elie Wiesel and the Scandal of Jewish Rage,”30 written in 1996, one year after the publication of Wiesel’s memoir All Rivers Run to the Sea, examines several passages in Night and compares them to passages in the Yiddish original. Among the relevant issues she brings up is this one:
Let me be clear: the interpretation of the Holocaust as a religious theological event is not a tendentious imposition on Night but rather a careful reading of the work.
In other words, Night presents the Holocaust as a religious event, rather than historical. In contrast, Siedman found that the Yiddish version, Un di Velt, published two years prior to the publication of Night, was similar to all others in the “growing genre of Yiddish Holocaust memoirs” which were praised for their “comprehensiveness, the thoroughness of (their) documentation not only of the genocide but also, of its victims.” Un di Velt Hot Gesvign was published as volume 117 of Mark Turkov’s Dos poylishe yidntum (Polish Jewry) in Buenos Aires.
Siedman refers to a reviewer of the mostly Polish Yiddish series when she writes:
For the Yiddish reader, Eliezer (as he is called here) Wiesel’s memoir was one among many, valuable for its contributing an account of what was certainly an unusual circumstance among East European Jews: their ignorance, as late as the spring of 1944, of the scale and nature of the Germans’ genocidal intentions. The experiences of the Jews of Transylvania may have been illuminating, but certainly none among the readers of Turkov’s series on Polish Jewry would have taken it as representative. As the review makes clear, the value of survivor testimony was in its specificity and comprehensiveness; Turkov’s series was not alone in its preference. Yiddish Holocaust memoirs often modeled themselves on the local chronical (pinkes ) or memorial book (yizker-bukh ) in which catalogs of names, addresses, and occupations served as form and motivation. It is within this literary context, against this set of generic conventions, that Wiesel published the first of his Holocaust memoirs.
Siedman continues that “Un di velt has been variously referred to as the original Yiddish version of Night and described as more than four times as long; actually, it is 245 pages to the French 158 pages.” But the “four times as long” was referring to the original 862 pages that Turkov cut down to 245. Siedman reminds us that Wiesel had earlier described his writing of the Yiddish with no revisions, “frantically scribbled, without reading.” She says this, and Wiesel’s complaint that the original manuscript was never returned to him, are “confusing and possibly contradictory.” She then writes:
What distinguishes the Yiddish from the French is not so much length as attention to detail, an adherence to that principle of comprehensiveness so valued by the editors and reviewers of the Polish Jewry series. Thus, whereas the first page of Night succinctly and picturesquely describes Sighet as “that little town in Transylvania where I spent my childhood,” Un di velt introduces Sighet as “the most important city [shtot] and the one with the largest Jewish population in the province of Marmarosh.” 31 The Yiddish goes on to provide a historical account of the region: “Until, the First World War, Sighet belonged to Austro-Hungary. Then it became part of Romania. In 1940, Hungary acquired it again.”
The great length of the original was no doubt due to the extensive detail it contained about the events, places and people that were the subject of the narrative. Despite the fact that descriptive detail is not a characteristic in any of Wiesel’s known writing, he would never have been able to write all that detail in two weeks in a ship’s cabin, relying only on his memory. He even says he saw no one during that time and cut himself off from everything. In the writing style of Elie Wiesel that we’re familiar with, what could he possibly have said to fill up 862 pages? Impossible!
Another point made by Siedman: And while the French memoir is dedicated “in memory of my parents and of my little sister, Tsipora,” the Yiddish (book) names both victims and perpetrators: “This book is dedicated to the eternal memory of my mother Sarah, father Shlomo, and my little sister Tsipora — who were killed by the German murderers.” 32 The Yiddish dedication is an accusation from a very angry Jew who is assigning exact blame for who was responsible. In addition, this brings to mind the fact that Elie Wiesel’s youngest sister was named Judith at birth, not Tsipora (according to his sister Hilda’s testimony).
Siedman says the effect of this editing from the Yiddish to the French was:
…to position the memoir within a different literary genre. Even the title Un di velt hot geshvign signifies a kind of silence very distant from the mystical silence at the heart of Night. The Yiddish title (And the World Remained Silent) indicts the world that did nothing to stop the Holocaust and allows its perpetrators to carry on normal lives […] From the historical and political specificities of Yiddish documentary testimony, Wiesel and his French publishing house fashioned something closer to mythopoetic narrative.
Myth and poetry … from a very historical and political original testimony. Wiesel attempted to explain this in his memoir by describing his French publisher’s objections to his documentary approach: “Lindon was unhappy with my probably too abstract manner of introducing the subject. Nor was he enamored of two pages (only two pages?) which sought to describe the premises and early phases of the tragedy. Testimony from survivors tends to begin with these sorts of descriptions, evoking loved ones as well as one’s hometown before the annihilation, as if breathing life into them one last time.” 33 Just how convincing that is I leave up to the reader.
The most controversial part of Siedman’s essay is about the Jewish commandment for revenge against one’s enemies. The author of the Yiddish writes that right after the liberation at Buchenwald:
Early the next day Jewish boys ran off to Weimar to steal clothing and potatoes. And to rape German girls [un tsu fargvaldikn daytshe shikses]. The historical commandment of revenge was not fulfilled.” 34
This reflects the same angry, stern Jew who demands the Jewish law of revenge upon one’s enemies be followed. He does not consider “raping German girls” to be sufficient revenge; thus he says the historical commandment was not fulfilled. In the French and English, it was softened to: “On the following morning, some of the young men went to Weimar to get some potatoes and clothes—and to sleep with girls. But of revenge, not a sign.”35 Siedman comments on this passage:
To describe the differences between these versions as a stylistic reworking is to miss the extent of what is suppressed in the French. Un di velt depicts a post-Holocaust landscape in which Jewish boys “run off” to steal provisions and rape German girls; Night extracts from this scene of lawless retribution a far more innocent picture of the aftermath of the war, with young men going off to the nearest city to look for clothes and sex. In the Yiddish, the survivors are explicitly described as Jews and their victims (or intended victims) as German; in the French, they are just young men and women. The narrator of both versions decries the Jewish failure to take revenge against the Germans, but this failure means something different when it is emblematized, as it is in Yiddish, with the rape of German women. The implication, in the Yiddish, is that rape is a frivolous dereliction of the obligation to fulfill the “historical commandment of revenge”; presumably fulfillment of this obligation would involve a concerted and public act of retribution with a clearly defined target. Un di velt does not spell out what form this retribution might take, only that it is sanctioned — even commanded — by Jewish history and tradition.
The final passage that Siedman compares is the famous ending of Night. The Yiddish version presents not only a longer narrative, but a radically different person who emerges from his camp experience at the time of liberation.
Three days after liberation I became very ill; food-poisoning. They took me to the hospital and the doctors said that I was gone. For two weeks I lay in the hospital between life and death. My situation grew worse from day to day.
One fine day I got up—with the last of my energy—and went over to the mirror that was hanging on the wall. I wanted to see myself. I had not seen myself since the ghetto. From the mirror a skeleton gazed out. Skin and bones. I saw the image of myself after my death. It was at that instant that the will to live was awakened. Without knowing why, I raised a balled-up fist and smashed the mirror, breaking the image that lived within it. And then — I fainted… From that moment on my health began to improve. I stayed in bed for a few more days, in the course of which I wrote the outline of the book you are holding in your hand, dear reader.
But—Now, ten years after Buchenwald, I see that the world is forgetting. Germany is a sovereign state, the German army has been reborn. The bestial sadist of Buchenwald, Ilsa Koch, is happily raising her children. War criminals stroll in the streets of Hamburg and Munich. The past has been erased. Forgotten. Germans and anti-Semites persuade the world that the story of the six million Jewish martyrs is a fantasy, and the naive world will probably believe them, if not today, then tomorrow or the next day.
So I thought it would be a good idea to publish a book based on the notes I wrote in Buchenwald. I am not so naive to believe that this book will change history or shake people’s beliefs. Books no longer have the power they once had. Those who were silent yesterday will also be silent tomorrow. I often ask myself, now, ten years after Buchenwald : Was it worth breaking that mirror? Was it worth it? 36
This entire passage sounds nothing like Elie Wiesel, or anything he has written. It is matter of fact, not indulging in self-pity but addressing the reality of the situation with a cynical eye. The author is concerned with the traditional problems of Jews, as he sees it, and their welfare. His “witness” as a survivor is not mystical or universalized, but is about assessing blame. His depiction of smashing the mirror that holds his dead-looking image, and how that expression of powerful anger and life-affirmation revived him, is convincing. Right away, he wants to write about his experience, and he begins. Anger and “putting it all down” is the way out of depression and listlessness.
Yet the author and editors of Night have removed almost all of this and end very differently:
One day I was able to get up, after gathering all my strength. I wanted to see myself in the mirror hanging from the opposite wall. I had not seen myself since the ghetto.
From the depths of the mirror, a corpse gazed back at me.
The look in his eyes, as they stared into mine, has never left me.37
No anger. No recuperation or recovery possible for this character. No closure. Elie Wiesel leaves us in Night with the image of death, and for the rest of his life he will pour it out on the world through his writings. This is his legacy; the Holocaust never ends.
Siedman comments on these two endings:
There are two survivors, then, a Yiddish and a French—or perhaps we should say one survivor who speaks to a Jewish audience and one whose first reader is a French Catholic. The survivor who met with Mauriac labors under the self-imposed seal and burden of silence, the silence of his association with the dead. The Yiddish survivor is alive with a vengeance and eager to break the wall of indifference he feels surrounds him.
Naomi Siedman intends the “two survivors” to be taken symbolically, as she is a “respected” Jewish academic who does not question the Holocaust story, and does not question (publicly at least) the authenticity of Elie Wiesel as the author of the Yiddish 862-page And the World Remained Silent, no matter what difficulties are encountered. As she continues in this essay, she posits Francois Mauriac’s powerful influence on Elie Wiesel as the way of explaining the further shortening and redirection of the focus of the original text. This is not my position, so I don’t find it profitable to seek for the origins of Night in Mauriac’s Catholic/Christian views. I believe there are sufficient grounds to consider a different authorship for Un di Velt Hot Gesvign, and that neutral-minded, critical thinkers who have an interest in this subject would not object to studying it from this angle.
However the grounds for doing so have not been exhausted by these two essays, so I will continue with a summing up in Part Three.
Endnotes:
15) Sanford Sternlicht, Student Companion to Elie Wiesel, Greenwood Press, Westport, CT, 2003, p. 3.
16) Ibid.
17) First Person: Life & Work. http://www.pbs.org/eliewiesel/life/index.html
18) All Rivers Run to the Sea, p. 9
19) First Person: http://www.pbs.org/eliewiesel/life/henry.html
20) Rivers, p. 20
21) http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/biography/Wiesel.html
22) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monsieur_Chouchani
23) Rivers, p. 121
24) Wikipedia, Chouchani
25) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Night_(book) Miklos Grüner says his 32-year-old friend Lazar Wiesel was given an apartment and an income because he had travelled with the orphans to France, under special permission. (see Stolen Identity by Grüner, printed in Sweden, 2007)
26) Wiki/Night
27) Jewish virtual library, ibid.
28) http://www.scribd.com/doc/33182028/STOLEN-IDENTITY-Elie-Wiesel
29) Grüner is speaking of Block 56, where what was to become the “famous Buchenwald liberation photograph” was taken by an American military photographer on April 16, 1945, five days after liberation. See our analysis of this photo under “The Evidence” on the menu bar.
30) “Elie Wiesel and the Scandal of Jewish Rage,” Seidman, ibid.
31) Eliezer Vizel, Un di velt hot geshvign (Buenos Aires, 1956), p. 7
32) Un di velt, n.p.
33) Rivers, p. 319
34) Un di velt, 244.
35) Night, 120.
36) Un di velt, 244-45
37) Night, 120.
11 Comments
Category Featured | Tags: Tags: Hasidic Jews, Miklos Grüner, Naomi Siedman, Night, Romania, Shushani/Chouchani, Sighet, Un di Velt Hot Gesvign, Zion in Kamf,
Social Networks: Facebook, Twitter, Google Bookmarks, del.icio.us, StumbleUpon, Digg, Reddit, Posterous.

 Danuta Czech, in her Auschwitz Chronicle1, records that on January 26,
Danuta Czech, in her Auschwitz Chronicle1, records that on January 26,
 Kenneth Waltzer also claims on his Michigan State University website that Elie Wiesel is “seen to the left” (short boy fourth from the front in left row wearing dark suit in front of the taller boy wearing a beret) in this photograph of the youths being transferred from the barracks inside Buchenwald to the former SS barracks on the outside. Why is Waltzer not paying attention to what is written in Night — that Eliezer was put in the hospital on the 14th of April, at death’s door, and remained for two weeks? One really has to wonder at the stupidity of holocaust historians. Or more likely — how stupid they think the rest of us are! See The Many Faces of Elie Wiesel.
Kenneth Waltzer also claims on his Michigan State University website that Elie Wiesel is “seen to the left” (short boy fourth from the front in left row wearing dark suit in front of the taller boy wearing a beret) in this photograph of the youths being transferred from the barracks inside Buchenwald to the former SS barracks on the outside. Why is Waltzer not paying attention to what is written in Night — that Eliezer was put in the hospital on the 14th of April, at death’s door, and remained for two weeks? One really has to wonder at the stupidity of holocaust historians. Or more likely — how stupid they think the rest of us are! See The Many Faces of Elie Wiesel.