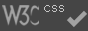Night #1 and Night #2—What Changes were Made and Why, Part One
Friday, February 17th, 2012
By Carolyn Yeager
copyright 2012 Carolyn Yeager
On Tuesday, January 17, 2006, Amazon.com announced that it was changing the categorization of a new translation of Elie Wiesel’s Night from novel to memoir.
Amazon would also revise the editorial description of the original edition to make clear that they consider the book a memoir, not a novel. “We hope to make these changes as quickly as possible,” said Jani Strand, a spokeswoman for the online retailer. The day before, Oprah Winfrey had announced that Night was her latest book club choice, displacing her previous selection, James Frey’s A Million Little Pieces.
 The sudden switch from fiction to non-fiction caused some discussion and questions, which Strand brushed away by saying, “Amazon.com’s data source for the Oprah Book Club edition of Night inaccurately classified the book as fiction.” She declined to offer details. The book, re-classified as “Autobiography” and blessed by Oprah, was already No.3 on Amazon.com as of that Tuesday afternoon! Wiesel, interviewed later with his literary agent Georges Borchardt, insisted they had never portrayed it as a novel.
The sudden switch from fiction to non-fiction caused some discussion and questions, which Strand brushed away by saying, “Amazon.com’s data source for the Oprah Book Club edition of Night inaccurately classified the book as fiction.” She declined to offer details. The book, re-classified as “Autobiography” and blessed by Oprah, was already No.3 on Amazon.com as of that Tuesday afternoon! Wiesel, interviewed later with his literary agent Georges Borchardt, insisted they had never portrayed it as a novel.
But the publisher did.1 There has been confusion about the question for so long—even Wiesel’s defenders have to admit it. Ruth Franklin, in her 2011 book, A Thousand Darknesses, wrote: “Unfortunately, Night is an imperfect ambassador for the infallibility of the memoir, owing to the fact that it has been treated very often as a novel—by journalists, by scholars, and even by its publishers.”2 On Night’s Wikipedia page it has long been described as autobiography, memoir, novel—yes, all three. How long will that continue? As long as there are editions of Night that still sport those labels, one assumes.
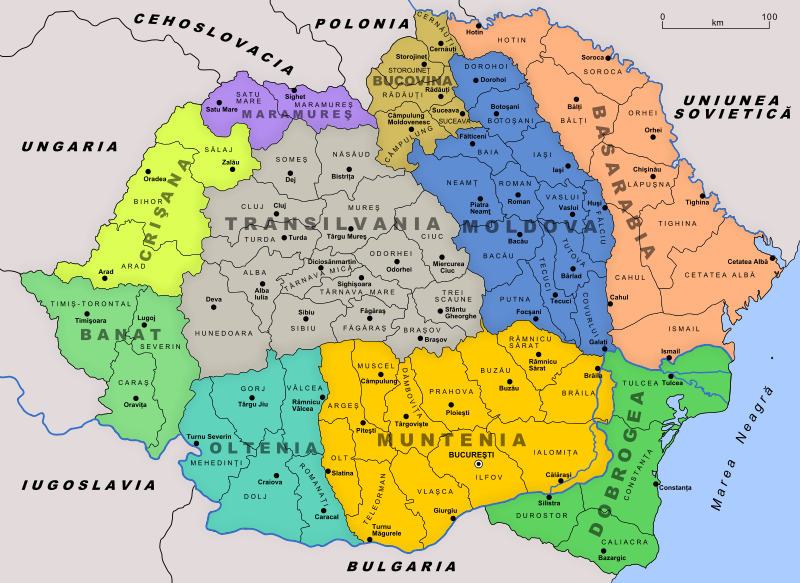
Left: Oprah Winfrey and Elie Wiesel pose together at the Elie Wiesel Foundation for Humanity Award Dinner at the Waldorf Astoria Hotel on May 20, 2007. Winfrey was honored with the Humanitarian Award for “positively impacting people all over the world, especially children.” One year earlier, she had selected Wiesel’s “Night” for her popular book club “pick” which sent it immediately to the top of the national bestseller lists.
As for Wiesel and Borchardt, they answered questions about differences in the text of the new edition by saying they were not significant enough to justify raising questions. The next day, Wiesel’s wife Marion, the translator of the new edition of Night, said in an interview that among the changes was a reference to the age of the book’s narrator when he arrives in 1944 at Birkenau, the entry point for Auschwitz.
 “At no point did this change the meaning and the fact of anything in the book,” Marion Wiesel said. She explained it this way: The narrator tells a fellow prisoner that he is “not quite 15.” But the scene takes place in Spring 1944. Mr. Wiesel, born on Sept. 30, 1928, would have already been 15, going on 16. So in the new edition, she changed it to “15.” Whaaaa? She changed the age of Eliezer as it was written in the Yiddish book to fit Elie Wiesel, who was fifteen and a half at that time. What is written in the Yiddish original, Un di velt hot geshvign, we also find in the original Night, so that can only be called unethical. Marion tried to joke it away, telling reporters “I kidded Elie and told him, ‘I don’t think you can add.'”
“At no point did this change the meaning and the fact of anything in the book,” Marion Wiesel said. She explained it this way: The narrator tells a fellow prisoner that he is “not quite 15.” But the scene takes place in Spring 1944. Mr. Wiesel, born on Sept. 30, 1928, would have already been 15, going on 16. So in the new edition, she changed it to “15.” Whaaaa? She changed the age of Eliezer as it was written in the Yiddish book to fit Elie Wiesel, who was fifteen and a half at that time. What is written in the Yiddish original, Un di velt hot geshvign, we also find in the original Night, so that can only be called unethical. Marion tried to joke it away, telling reporters “I kidded Elie and told him, ‘I don’t think you can add.'”
But that particular change, rather than insignificant, was one of the major reasons that a new translation was undertaken. There are other quite significant changes in the new edition that will be enumerated in this article. When you learn what they are, you can decide for yourself if you think they are insignificant.
Right: Marion Wiesel is the translator of the 2006 edition of Night. Here, in 2010, she attends an after party at The Monkey Bar for Oliver Stone’s new “South of the Border” New York premiere at Cinema 21.
Wiesel wrote a Preface to the New Translation, something he didn’t have in the original La Nuit or Night.
In his preface, Wiesel begins: “Why did I write it? … so as not to go mad or, on the contrary, to go mad in order to understand the nature of madness …”
He continues in this vein—typical Wiesel mystical-religious style. However, in his only description of the writing process of this book—the typing of the 862 pages which he titled Un di velt hot geshvign, according to his later memoir—it is hard to believe that he was in such a state of mind. He writes in All Rivers Run to the Sea that during this time in Paris he is busy with his newspaper job and contacts; also involved in a love affair with a woman named Hanna. He embarks on a major journalistic assignment in Brazil, sent by his editor, taking along a friend to keep him company on the ship’s crossing. They both get free tickets from a “resourceful Israeli friend”—these benefactors are usually unnamed. As the voyage begins, he says his mind is dwelling on Hanna and whether he should take the marriage step that she had asked for.
I can’t imagine an atmosphere less conducive to writing about what he describes as “the immense, terrifying madness that had erupted in history.” But he continues very matter-of-factly in All Rivers, “During the crossing I wrote my testimony …” and in one short paragraph tells us all he thought important to say about it. Moreover, he has never elaborated on it since!
In the new preface, Wiesel writes that in retrospect he doesn’t know what he wanted to achieve with his words, but then he comes up with something: “I knew that I must bear witness. I also knew that, while I had many things to say, I did not have the words to say them.” He needed to “invent a new language.” He is not speaking of an actual language, like German, French or English—but a language of survivors, or for survivors. Wiesel writes that common words like “hunger—thirst—fear—transport—selection—fire—chimney … all have intrinsic meaning, but in those times, they meant something else.” Really? He does not explain how that is so. But Wiesel has tried to create the idea of holocaust survivors as a special class, set apart, who know things others do not know, and can never understand—”Only those who experienced Auschwitz know what it was. Others will never know.”
Wiesel describes his writing as slow! “Writing in my mother tongue (Yiddish) … I would pause at every sentence, and start over and over again. I would conjure up other verbs, other images, other silent cries. It still was not right.” This contrasts totally with his description in his memoir All Rivers Run to the Sea (p. 238-40) that he wrote the original Yiddish manuscript fast and feverishly without re-reading!
Why a new translation of Night after 45 years of success with the old one?
Here again, Wiesel hedges in the preface and doesn’t have a convincing answer. He says his wife Marion has translated other books for him, and “knows his voice better than anyone else.” He says he didn’t pay enough attention to the original English translation by Stella Rodway—after his first reading of Night from the publisher, he never read it again. As for Mrs. Wiesel: “Fluent in French, she had never read the English version,” she said. But good news! Elie Wiesel Cons The World has found a translator and now has large portions of the Yiddish book translated into English. We can compare the real 245-page original to both the 1960 English translation from the French by Stella Rodway and the 2006 English translation done by Marion Wiesel.
In doing so, we have made two important discoveries.
First, Stella Rodway’s 1960 English translation of Night is an accurate rendition of the French text of La Nuit, as originally published in 1958. That means that if there are any “errors” in the Night story, they weren’t put there by Stella Rodway.
Second, when we compare the three texts—the original version of Night, as translated by Rodway, the “corrected” 2006 translation by Marion Wiesel, and the 1955 Yiddish original of Un di velt hot geshvign—we find that the “errors” brought up by Marion Wiesel are for the greater part what was actually written in the original Yiddish book, though usually in more detail there.
In other words, the 1955 Yiddish version, the 1958 French version, and the 1960 English version generally agree—only the “corrected” 2006 translation is different. So, are these really errors of translation that Marion Wiesel is fixing for us? Or are they not simply problems for Elie Wiesel? Under close scrutiny, the Elie Wiesel narrative has huge holes which bring up embarrassing questions, and this is what Marion Wiesel’s new translation was meant to head off.
Left: Original Night cover, 1960, features the title, while the author’s name is exceptionally small and insignificant. Francois Mauriac’s forward is featured. In 2006, the author becomes the “title,” i.e. the main selling point, and Mauriac is no longer mentioned, although his forward remains in the book.
A Comparison of the 1960 original with the 2006 new version.
Following are the most “significant” differences I have found between the Stella Rodway 1960 translation and the Marion Wiesel 2006 translation. To make as clear a case as possible, I begin with the Yiddish [UdV] and its French translation La Nuit [LN], followed by the Stella Rodway English translation [SR]. Finally, Marion Wiesel’s revised translation [MW]. The word or phrase being compared is in boldface. Number one has already been written about in When Did Elie Wiesel Arrive at Auschwitz?
1. The Saturday before Pentecost … or two weeks before?
UdV Page 22: Geshen iz dos Shbth far Shbw’wth. A friling-zun hot oysgegosn ir likht un varemkeyt iber der gorer velt un oykh iber geto … / It happened Saturday [Sabbath] before Shavuot. The springtime sun had spread its light and warmth over the whole world, and even over the ghetto. . . .
LN Page 29: Le samedi précédant la Pentecôte, sous un soleil printanier, les gens se promenaient insouciants à travers les rues grouillantes de monde / The Saturday preceding Pentecost …
SR Page 23: On the Saturday before Pentecost, in the Spring sunshine, people strolled carefree and unheeding, through the swarming streets.
MW Page 12: Some two weeks before Shavuot (Pentecost). A sunny spring day, people strolled seemingly carefree through the crowded streets.
The Yiddish, the French and the original English versions agree—it was the Saturday before the festival of Pentecost/Shavuot—but Marion Wiesel’s new edition sets that date back by two whole weeks. This is very significant because, as the story continues, it was later on the following day that the Jews of Sighet were forced to leave their homes in preparation for their eventual deportation: “The ghetto was to be liquidated entirely. We were to leave street by street, starting the following day.”
So Mrs.Wiesel was NOT correcting errors in the English translation, but changing the text to fit the reality of when the Hungarians from Sighet arrived at Birkenau. Pentecost was on Sunday, May 28, 1944. The “Saturday before Pentecost” is thus May 27. Some two weeks before is May 14.
Un di velt hot geshvign, La Nuit and the Rodway translation all have Eliezer’s family leaving on the final journey to Auschwitz around June 2nd, six days after Pentecost/Shavuot, which was a Friday. However, they also agree that “Saturday, the day of rest, was chosen for our expulsion.” So it’s necessary for us to add another day to the family’s stay in the small ghetto to make the chronology work. On Saturday, then, the Jews are marched to the synagogue and spend the night there; in the morning, Sunday June 4, they board the train: “The following morning [Sunday], we marched to the station, where a convoy of cattle wagons was waiting. [… ] We were on our way.” Four days and three nights on the train (according to the description in Night) makes their arrival date June 6, 1944, around midnight.
But this is not only long after the prisoner number A7713—which Elie Wiesel supposedly received at Auschwitz, and still (again, supposedly!) has tattooed on his left arm—had been given out, but also long after the last transport left from Sighet. Indeed, there were no transports from the town after May, according to official records.
Marion Wiesel did not mention this one to the reporters; nor did Elie speak of it in his preface to his wife’s translation. But it was discovered by our translator. Marion Wiesel’s arbitrary “correction” allows Eliezer’s family to leave on May 21 and to arrive by May 24 (just before midnight!) thus making it possible for Eliezer to receive the registration number A7713. This is a very significant change, probably the most significant in her entire new English translation.
An added note: This interesting passage is on page 27 of Un di velt, but is not included in the shorter French or English Night:
We had opportunities and possibilities to hide with regular goyim and with prominent personalities. Many non-Jews from the surrounding villages had begged us, that we would come to them. There were bunkers available for us in villages or in the mountains. But we had cast aside all proposals. Why? Quite simple: the calendar showed April 1944 and we, the Jews of Sighet, still knew nothing about Treblinka, Buchenwald and Auschwitz.
Now we have April as the general time of deportation! So according to the timeline we find in Un di velt, Eliezer and his family left Sighet some time in June, while the calendar on their wall still said April . . . and in the meantime, we know from official Auschwitz records that the deportations actually occurred in the last two weeks of May. The person who wrote this knew nothing about the real deportation dates for the Sighet Jews.
2. Copulating on the train … or just caressing?
UdV Page 47: Tsulib der engshaft hobn a sakh instinktn zikh dervekt in kerper. Erotishe instinktn, un untern forhang fun der nakht hobn yungeleyt un froyen zikh gelozn bahersht durkh di oyfgereytste chwshym zeyere.
Ot der ershter rezultat fun umglik: erotishe freyheyt. Di shpanung fun di letste teg hot itst gezukht a veg vi oystsulodn zikh un der leychtster iz geven – an erotisher.
Di erotishe stsenes hobn nisht dervekt keyn protestn mtsd di eltere Yidn. Zey hobn farmakht oyern un oygn, zikh gemakht nisht zen un nisht hern. In moment fun schnh faln avek di keytn fun der konventsioneler moral. Mentshn hobn zikh getrakht: ver veys vos der morgn iz “lwl tsu brengen? Zol yugnt oysnutsn dem heynt, oystsapn fun im dem letstn hn’h-tropn . . .
In English: Because of the crowding, a host of instincts awoke in [people’s] bodies. Erotic instincts – and beneath the curtain of night young men and women let themselves be ruled by their aroused senses.
And so the first result of misfortune: erotic freedom. The stress of the last days now sought a way to discharge itself, and the easiest was – an erotic one.
The erotic scenes did not arouse any protests from the older Jews. They closed their ears and eyes, and forced themselves not to see and hear. In the moment of danger, the chains of conventional morality fall away. People thought to themselves: who knows what the morning is likely to bring? Youth must seize the day, squeeze from it the last drops of pleasure . . .
LN Page 45: Libérés de toute censure sociale, les jeunes se laissaient aller ouvertement à leurs instincts et à la faveur de la nuit, s’accouplaient au milieu de nous, sans se préoccuper de qui que ce fût, seuls dans le monde. Les autres faisaient semblant de ne rien voir.
SR Page 34: “Free from all social constraint, the young people gave way openly to instinct, taking advantage of the darkness to copulate in our midst, without caring about anyone else, as though they were alone in the world. The rest pretended not to notice anything.”
MW Page 23: “Freed of normal constraints, some of the young let go of their inhibitions and, under cover of darkness, caressed one another, without any thought of others, alone in the world. The others pretended not to notice.”
Elie Wiesel did not mention this change in his preface to the new English translation by his wife, but he did give quite a lengthy explanation (humorous to us) in the preface he wrote for the new French edition. This is what he said there:
Thanks to her, it was possible for me to correct an incorrect expression or impression here and there. An example: I describe the first night-time voyage in the sealed cars, and I mention that certain persons had taken advantage of the darkness to commit sexual acts. That’s false. In the Yiddish text, I say that “young boys and girls allowed themselves to be mastered by their excited erotic instincts.” I have checked among many absolutely trustworthy sources. In the train, all the families were still together. A few weeks of the ghetto could not have degraded our behavior to the point of violating customs, mores and ancient laws. That there may have been some clumsy touching, that is possible. But that was all. Nothing went any further. But then, why did I say that in Yiddish, and allow it to be translated into French and English? The only possible explanation: it is myself I am speaking of. It is myself that I condemn. I imagine that the adolescent that I was then, in the throes of puberty even if profoundly pious, could not resist such erotic imaginings, enriched by the physical proximity between men and women.
The original French : Grâce à elle, il me fut permis de corriger çà et là une expression ou une impression erronées. Exemple : j’évoque le premier voyage nocturne dans les wagons plombés et je mentionne que certaines personnes avaient profité de l’obscurité pour commettre des actes sexuels. C’est faux. Dans le texte yiddish je dis que « des jeunes garçons et filles se sont laissés maîtriser par leurs instincts érotiques excités. » J’ai vérifié auprès de plusieurs sources absolument sûres. Dans le train toutes les familles étaient encore réunies. Quelques semaines de ghetto n’ont pas pu dégrader notre comportement au point de violer coutumes, moeurs et lois anciennes. Qu’il y ait eu des attouchements maladroits, c’est possible. Ce fut tout. Nul n’est allé plus loin. Mais alors, pourquoi l’ai-je dit en yiddish et permis de le traduire en français et en anglais? La seule explication possible: c’est de moi-même que je parle. C’est moi-même que je condamne. J’imagine que l’adolescent que j’étais, en pleine puberté bien que profondément pieux, ne pouvait résister à l’imaginaire érotique enrichi par la proximité physique entre hommes et femmes.
Is this convincing, dear readers? Consider that the narrator of Un di velt says exactly the opposite of what Wiesel tries to present in his new French preface: the first result of a few weeks in the ghetto was erotic freedom, which was acted out in front of everyone in the train. And the “erotic instincts” that the youths let themselves be “ruled by” clearly must have involved sexual intercourse—why else would everyone have needed to shut their eyes and ears so tightly?
The Elie Wiesel of 2006 (and perhaps the Hasidic rebbes had something to do with this?) wants us to believe in the inviolable sanctity of the Jews’ “customs, mores and ancient laws,” and also in their innate respect for their elders and one another. But he is directly contradicted by what are, we are told, his own words of fifty years ago : “In the moment of danger, the chains of conventional morality fall away.” Which Wiesel do we believe?
And Ruth Franklin, senior editor at The New Republic, has the temerity to insist (toward the end of her 2006 review article) that “his [Elie’s] original suggestion that couples “copulated” in the cattle cars on the way to Auschwitz . . . was always a gross mistranslation of the original Yiddish.” We’ve shown you here that it isn’t.
3. Not yet fifteen … or fifteen?
UdV Page 63 : Yingl, vi alt bistu? fregt mir a heftling. Zeyn pnym iz geven in der fintster, ober zeyn kol iz geven a mids, a varems. Nokh nisht keyn 15 yor, hob ikh geentfert.
“Kid, how old are you?” a prisoner asked me. His face was in darkness, but his voice was tired and warm. “Not yet 15 years,” I answered.
LN Page 54: Hé, le gosse, quel âge as-tu? C’était un détenu qui m’interrogeait. Je ne voyais pas son visage, mais sa voix était lasse et chaude. “Pas encore quinze ans.” / Not yet 15 years.
SR Page 39: “Here, kid, how old are you?” It was one of the prisoners who asked me this. I could not see his face, but his voice was tense and weary. “I’m not quite fifteen yet.”
MW Page 30: “Hey, kid, how old are you?” The man interrogating me was an inmate. I could not see his face, but his voice was weary and warm. “Fifteen”
This very important passage was discussed above. I think the reader would agree that “not yet 15″ can mean even farther from the age of 15 than “not quite fifteen.” What is clear is that Marion Wiesel has changed the author’s original words to fit them to her husband’s age in Spring 1944.
4. April … or May?
UdV Page 83: A sheyner April-tog iz es geven. A frilings-rich in der luft. In English: It was a beautiful April day. A scent of spring in the air.
LN Page 69: C’était une belle journee d’avril. Des parfums de printemps flottaient dans l’air. Le soleil baissait vers l’ouest.
SR Page 49: It was a beautiful April day. The fragrance of spring was in the air. The sun was setting in the west.
MW Page 40: It was a beautiful day in May. The fragrances of spring were in the air. The sun was setting.
(See again When Did Wiesel Arrive) Once more, the original Night as translated by Stella Rodway agrees with the Yiddish and the French; Marion Wiesel arbitrarily changed April to May, yet said her translation did not “change the meaning or the fact of anything in the book” … what she calls a “significant change.” Well, this is a significant change, and for the same reason as given in number 1 above.
5. Himmler … or “Reichsfuehrer Himmler?”
UdV Page 124-5: “In nomen fun Himler . . . der heftling num’ . . . hot gegnbet . . . bsh”thn luft-alarm . . . loytn gezets, paragraf . . . iz der heftling num’ . . . farurteylt tsum toyt! Zol dos zeyn a lere un a beyshpil far ale heftlingen . . .”
“In the name of Himmler . . . prisoner number . . . stole . . . during the air raid . . . according to the law, paragraph . . . prisoner number . . . is condemned to death. May this be a lesson and an example for all prisoners.”
LN Page 100: “Au nom de Himmler ... Le détenu No… a dérobé pendant l’alerte… “
SR Page 68: “In the name of Himmler … prisoner Number … stole during the alert … According to the law … paragraph …prisoner Number … is condemned to death. May this be a warning and an example to all prisoners.”
MW Page 62: “In the name of Reichsfuehrer Himmler … prisoner number … stole during the air raid … according to the law … prisoner number … is condemned to death. Let this be a warning …..”
Again, the Yiddish and the original Night agree. However, no trained member of the SS, or even the Wehrmacht, would ever have shown such disrespect as to use Himmler’s name in such a formal context without his full title: Reichsfuehrer SS Heinrich Himmler. Marion Wiesel tried to fix the error by adding “Reichsfuehrer,” but she still gets it wrong: you don’t drop the “SS.” On its own, this tells us that the speech was an imaginary one invented by the author (whoever that is), someone who was never present at such a scene. Indeed, lack of knowledge about how the SS functioned in the camps is evident throughout the book. For example, the SS did not normally go inside the barracks; everything inside was handled by the kapos.
6. Ten days and ten nights … or just “days and nights”
UdV Page 207: Tsen teg un tsen nekht hot gedoyert di reyze. / Ten days and ten nights the trip lasted.
LN Page 155: Dix jours, dix nuits de voyage. Il nous arrivait de traverser des localités allemandes.
SR Page101: Ten days, ten nights of traveling. Sometimes we would pass through German townships.
MW Page 100: There followed days and nights of traveling. Occasionally we would pass through German towns.
In January of 1945, as the advancing Red Army approached Auschwitz, a decision was made to evacuate, sending the prisoners to other camps in Germany. Evacuation of the Monowitz (Auschwitz III) camp, to which Eliezer and Father had previously been transferred, began at 6 p.m. on January 18. The prisoners were given extra clothing and food—bread to carry with them. They also had whatever food they had saved up. After marching all night during a snowfall, they rested in the morning in an old brick factory. In late afternoon, they began again and reached Gleiwitz camp in a few hours [night, Jan. 19]; they then remained in Gleiwitz barracks for three days. On the 22nd they went to the train stop and waited until evening. They were brought bread for the journey. The convoy set out
From there, as we see above, the Yiddish, the 1958 French and 1960 English versions agree on the trip lasting ten days and nights. But Marion Wiesel removes the number ten because it makes Eliezer’s timeline for the death of his father on Jan. 28/29 completely impossible. Another very significant change. Ten days and nights from the night of Jan. 22nd is the night of Feb 1, 1945.
This shows that the author of Un di velt knew nothing about the transport that arrived at Buchenwald on January 26 with 3000 prisoners from Auschwitz. This is the transport that, according to existing official records, brought Lazar and Abraham Wiesel to Buchenwald, who were registered at the camp there on . . . January 26, 1945! (See Buchenwald Archivist Cannot ID Elie Wiesel, How True to Life is Wiesel’s description of Buchenwald, and Gigantic Fraud Carried Out.)
7. Fifteen … or sixteen?
UdV Page 213: I was fifteen years old then. Do you understand—fifteen? Is it any wonder that I, along with my generation, do not believe either in God or in man; in the feelings of a son, in the love of a father. Is it any Wonder that I cannot realize that I myself experienced this thing, that my childish eyes had witnessed it? (This passage from Moshe Spiegel’s stand-alone translation of Chapter Six of Un di velt hot geshvign, published as “The Death Train” in the 1968 volume Anthology of Holocaust Literature.)
LN Page 158: J’avais quinze ans. / I was fifteen.
SR Page 103: I was fifteen years old.
MW Page 102: I was sixteen.
In the original versions, Eliezer repeats that he is fifteen years old in January 1945. Elie Wiesel’s birth date is Sept. 30, 1928 so on that day in 1944 he became sixteen years old, making him 16 years and 4 months when this particular event on the train to Buchenwald occurred in late January 1945. Once again, Marion Wiesel simply changes the age as she did before — if Elie was actually sixteen at that time, then Eliezer, the character in the book, must be too!
In Part Two, I will construct the timeline of the events in Buchenwald following the arrival of Eliezer and his father, and other details about Buchenwald. What will we find out? Stay tuned.
Endnotes:
1. On the back cover of the original hardcover Night, with the black & white striped jacket (as pictured here), it is printed “Literature” as the classification.
2. Ruth Franklin, A Thousand Darknesses: Lies and Truth in Holocaust Fiction, Oxford University Press, 2011, pp 71-72.
Unfortunately, Night is an imperfect ambassador for the infallibility of the memoir, owing to the fact that it has been treated very often as a novel—by journalists, by scholars, and even by its publishers. Lawrence Langer, in his landmark study The Holocaust and the Literary Imagination, notes that Night “continues to be classified and critically acclaimed as a novel, and not without reason.” . . .
Nonetheless, in 1997 Publishers Weekly columnist Paul Nathan had to issue a correction apologizing for referring to the book as an “autobiographical novel”; he had been misled, he said, by the entry on Wiesel in The International Dictionary of Twentieth-Century Biography. In response, the correction itself was challenged by the director of Penguin Reference Books, publishers of the biography dictionary, who cited half a dozen sources to the effect that Night was in fact a novel. Together with most critics, Gary Weissman, who recounted the above history in his book Fantasies of Witnessing: Postwar Efforts to Experience the Holocaust, seems to concur with Ernst Pawel’s remark in an early magazine survey of Holocaust fiction, that “the line between fact and fiction, tenuous at best, tends to vanish altogether in autobiographical novels such as Night.” The hybrid terms used to describe it include “novel/autobiography,” “non-fictional novel,” “semi-fictional memoir,” “fictional-autobiographical memoir,” “fictionalized autobiographical memoir,” and “memoir-novel.
Category Featured | Tags: Tags: Auschwitz-Birkenau, Buchenwald, Elie Wiesel, Holocaust fraud, Marion Wiesel, Monowitz, Night, Oprah Winfrey, Ruth Franklin, Un di velt hot geshvign,
Social Networks: Facebook, Twitter, Google Bookmarks, del.icio.us, StumbleUpon, Digg, Reddit, Posterous.