How true to life is Wiesel’s description of Buchenwald in Night?
Monday, July 18th, 2011
By Carolyn Yeager
Ken Waltzer wrote in his comment on this blog on June 27th:
“More important, Elie Wiesel’s commentary in Night bears fairly close resemblance to the actual experiences he had at Buchenwald—as recorded in camp documents.” (my italics)
What are we to make of the words “fairly close resemblance?” According to Waltzer—and to Wiesel—Wiesel is writing down his own experience. “Every word is true!” Wiesel has said of his book Night. Thus it should exactly resemble the actual experience he had. I’m going to examine closely what is written in Night about Buchenwald to see if that is the case.
It’s not too difficult because the newest English edition of Night1—a new translation by wife Marion Wiesel which changes (corrects) some of the more blatant “boo-boos” found in the original 1960 edition—comprises only 115 pages. Of that, Wiesel’s description of his time at Buchenwald begins on page 104, giving it only 11 pages (one page being blank).
Wiesel wrote a new preface for this new translation in which he tries to answer some of the more common criticisms of his book. His answer to the differences between the Yiddish And the World Remained Silent and Night is that he cut passages he thought might be superfluous … or “too personal, too private, perhaps.” Strange thing to say since he had already published it. Concerning Buchenwald, he quotes the original writing about the death of his father, where the club-wielder is called “an SS” three times! In Night, as you will see below, this person becomes simply “an officer.” Naturally I ask: Did this scene even happen? Wiesel also tries to explain why he cut out from the ending so much of what was in the Yiddish version, but in doing so he leaves unmentioned an extensive part of what he cut. I have quoted these two endings in Shadowy Origins of Night, Part II.
Wiesel begins his experience at Buchenwald by writing that upon reaching the entrance to the Buchenwald camp along with his father and all the new arrivals from his transport, the SS counted them and they were directed to the Appelplatz (roll call area inside the camp) where loudspeakers ordered “Form ranks of fives! Groups of one hundred! Five steps forward!” He then writes, “A veteran of Buchenwald (as he puts it), told us that we would be taking a shower and afterward be sent to different blocks.” He makes it sound as if it were one of those among them, but it actually had to be a Kapo.
He writes that hundreds of prisoners crowded the shower area and made it difficult to get in, therefore his father wanted to find a place to sit down and wait—which he did in a pile of snow where there were other ‘bodies’ sticking out. Dead or alive we’re not told. It’s one of those literary scenes wherein Eliezer confronts Death via his fear of his father’s death. He writes: “This discussion (with his father) continued for some time.” Then … “sirens began to wail … lights went out … guards chased us toward the blocks.” They obviously did not get a hot shower. Wiesel adds: “The cauldrons at the entrance found no takers.” 2
Are we to believe that the kapos, or “veterans of Buchenwald,” allowed non-disinfected, non-showered new arrivals into the barracks, possibly carrying lice and other vermin with them? No way could this have happened. Yet Wiesel writes: “We let ourselves sink into the floor. To sleep was all that mattered.” I guess it was okay because they didn’t get into the beds.
In the morning, having lost track of his father the night before, he went to search for him. What about the regimentation? What about the early morning roll call? Wiesel writes: “I walked for hours without finding him. Then I came to a block where they were distributing black ‘coffee.’ ” 3 He heard his father’s voice asking for some coffee. He brought it to him. “He was lying on the boards,” meaning, I suppose, a bare bunk. Then, “We had been ordered to go outside to allow for cleaning of the blocks (barracks). Only the sick could remain inside. (If that was the case, they were not fumigating.) We stayed outside for five hours. We were given soup. When they allowed us to return to the blocks, I rushed toward my father” … who told Eliezer he had not been given any soup because “they said we would die soon and it would be a waste of food.”
Apparently, he stayed with his father in that barracks, making sure he was fed. Were they allowed to live in whatever barracks they chose? Again, there is no explanation given for this. He then writes that on the third day after their arrival everybody had to go to the showers, even the sick. Having done that (with no description of the process at all), they again had to wait “a long time” outside the barracks while they were being cleaned.
He fills a couple of pages with scenes of watching his father deteriorate amidst all the heartlessness. Then, after a week, a Blockälteste (block warden) told him he couldn’t save his father and he should help himself by eating his father’s rations. Instead, he pretends to be sick so he can stay in the barracks with his father. He doesn’t go to roll call. Now comes the famous passage in which he writes: “In front of the block, the SS were giving orders. An officer passed between the bunks. My father was pleading: “My son, water…I’m burning up…My insides …” The officer shouts at him to be quiet, walks over with a club and hits him “a violent blow to the head.” On that night, January 28, 1945, his father allegedly died.
The main problems with reality in this passage are:
1) The SS is known to have not been active inside the camp; the prisoner-trustees, usually communists, took care of giving the prisoners their orders. So the SS would not be in front of the block giving orders.
2) “An officer” can only be an SS officer. But they never came inside the barracks. Inmates, no matter how much “in charge” they might be, were not called officers. So who was this mysterious “officer” who was inside the barracks? Not SS at all; just part of the fiction and another attempt to assign brutalities to the SS.
Eliezer says he did not weep for his father. He was numb. He was transferred to the children’s block, where he remained with 600 others until April 11. That’s two and a half months, yet he tells us nothing of that time except that he did have an appetite and his only interest was getting an extra ration of soup. On April 5 (he knew the exact date) “we were inside the block, waiting for an SS to come and count us. He was late. Such lateness was unprecedented in the history of Buchenwald.”
Same problem as above: the official story (and Waltzer’s story) tells us that the communist “veterans” had these boys hidden away in the “small camp” where they cared for them, keeping them away from the SS and the camp authorities. We know that the SS did not go inside the blocks. Yet Wiesel writes that they did every day because on this day they were late. Covering for Wiesel, Waltzer writes on his website:
…the 16-year old Wiesel was assigned to a special barracks that was created and maintained by the clandestine underground resistance in the camp as part of a strategy of saving youths. This block, Block 66, was located in the deepest part of the disease-infested little camp, a separate space below the main camp at Buchenwald that was beyond the normal Nazi SS gaze (the local SS officer actively cooperated and conducted appels inside the barracks).
The barracks was overseen by block elder Antonin Kalina, a Czech Communist from Prague, and his deputy, Gustav Schiller, a Polish-Jewish Communist originally from Lvov. Odon Gati, a Communist from Budapest, was stubendienst. Schiller, who appears briefly in “Night,” was a father figure and mentor, especially for the Polish-Jewish boys and many of the Czech-Jewish boys, but he was less liked, and even feared, by Hungarian- and Romanian-Jewish boys, especially religious boys, including Wiesel. He appears in “Night” as a menacing figure, armed with a truncheon.
First, Waltzer mentions the underground. But they did not have the power to hide away the youths who were assigned to the special barracks 66. It was a policy of the Camp Commandant to separate these children to keep them safe, to feed them as well as possible, and they were fully aware of the children’s barrack 66 where they were kept. Thus. there may have been a “local SS officer” assigned to look after Block 66 to make sure everything was being done according to regulations … that is, even to supervise, to some extent, the communist block leaders. The story that it was the communists who “saved these boys from death” is a fiction that was created later, after the liberation of the camp and the formation of the Buchenwald association which was made up of former prisoners of communist persuasion. It was the camp authorities who made the decision to place the “children” away and apart from the adult prisoners, not the underground resistance.
Second, Wiesel writes in Night, “Gustav, the Blockälteste, made it clear with his club” that they had to obey the order to gather in the Appelplatz. Doesn’t this imply that the communist overseers were not necessarily acting as “father-figures” and mentors, but simply as guards? Also note that the kapo Gustav was carrying a club and used it, while earlier it was an “officer” in the barracks who wielded a club against Eliezer’s father. Relative to this, Ferenc Kornfeld reports : “Without exception, the Kapos all had big sticks.” He also said a Kapo armband went with a double food ration. And, “They continually shouted and they hit people on the head and the neck.” Kornfeld wrote about Buchenwald: “There were common criminals, murderers and thieves, in concentration camps too. They were called the “Blockältesters”. They were the “Kapos” (bosses). As they were murderers, they had black triangles on their uniforms. The Kapos hit and slapped all of us.” So much for the idea of Blockälteste’s as mentors.
The abrupt ending of Night
Wiesel claims on pages 114-15 (the last two pages of the book) that on April 5 everyone, even the children, were ordered to gather in the Appelplatz. On the way, some prisoners told them to go back because the Germans planned to shoot them. They turned around and on the way back they learned that “the underground resistance of the camp had made the decision not to abandon the Jews and to prevent their liquidation.” What kind of nonsense is this? Well, it is “the story” which evolved that these communists at Buchenwald finally, on the very last day, fought the Germans. What really happened was the Germans were ready to abandon the camp on the 11th, which they did. Wiesel simply picks up that official fiction of the underground resistance and incorporates it into his narrative. I don’t think the Germans ever intended to evacuate the children and youths.
Apparently, after the 5th, blocks of prisoners were being evacuated to other camps. By April 10, Wiesel writes, “we had not eaten for nearly six days except for a few stalks of grass and some potato peels found on the grounds of the kitchen.” From whom did these potato peels come? Did their communist keepers gather them and bring them to the youths inside the barracks? Did the boys roam around freely and eat grass? At ten o’clock the next morning, he tells us, the SS positioned themselves around the camp and began to herd the remaining inmates toward the Appelplatz. At this point the underground resistance members appeared “from everywhere” with guns and grenades. Eliezer and the other children “remained flat on the floor of the block.” (Therefore they saw nothing.) By noon, the SS had fled and the resistance was in charge. The first American tank arrived at 6 p.m.
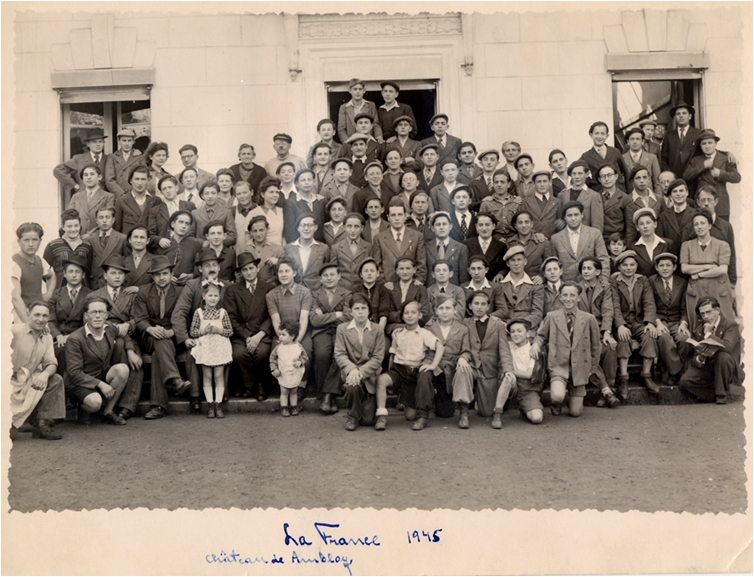
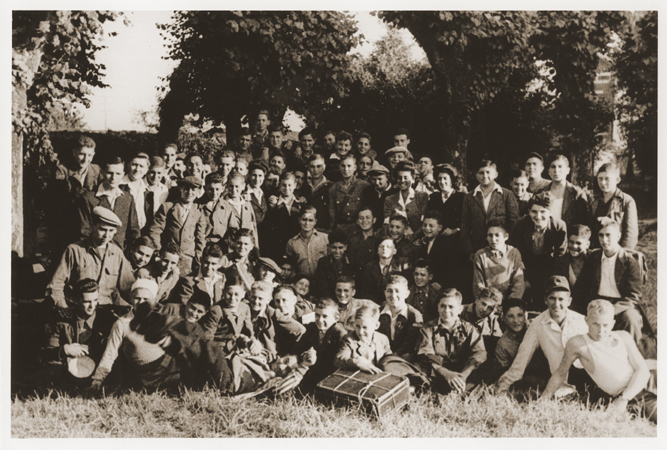
Wiesel now wastes no time in concluding the book. He says he became very ill from food poisoning three days later because they “threw themselves on the provisions.” He spent two weeks in the hospital “between life and death.” One day he got up and looked in a mirror and saw only a corpse gazing back at him. This was at the end of April or first of May 1945. Yet he recovered so well that we see a healthy, smiling boy in the picture supposedly taken of him at Ambloy in late 1945 … or is it early or mid 1946?
It’s interesting that Wiesel made such a point later on of maintaining he had vowed in 1945 to wait ten years to write down his experiences. The reasons given, including that his memory would be sharper after ten years, are completely bogus—especially since his book bears little resemblance to the actual camps as we know them to be. The much longer Yiddish version was published in 1955-56. The abridged French version La Nuit in 1958; the English Night in 1960.
Conclusions
I have to say Wiesel doesn’t describe Buchenwald at all. You don’t know anything about Buchenwald from reading Night. You don’t learn much about Eliezer or anyone else. You are given an impression of suffering, without rhyme or reason, so Buchenwald becomes synonymous with suffering, that’s about it. We don’t know what it looks like. We don’t know the name or the physical appearance of any person, not even Gustav carrying a club, who is said elsewhere to have had red hair. Wiesel makes up a story about “an officer” using a club in the barracks when it could only be a kapo (if it was anyone at all). He doesn’t tell us anything about the children in the barracks where he stayed for 2 ½ months. He doesn’t describe the few days after liberation, before he got sick. One did not have to be at Buchenwald to write what he wrote!
Ken Waltzer also writes at his website:
Elie Wiesel has acknowledged the role played by the clandestine underground and political prisoners in saving children and youth at Buchenwald, especially in his autobiography, but he did not attend to this in “Night.” It was not his purpose or focus in that book. Many of his fellow barracks members, however, who are still alive and remember very well their days and nights in Block 66; their relations with Kalina, Schiller and others; and the hope provided to them there, have been helping fill in the story.
You can see a couple of these fellow barracks members here: Scroll down for Excerpts from the “Boys of Buchenwald” discussion panel (7.45 minutes) You can judge for yourself how impressive they are…or not. Neither one mentions Elie Wiesel.
Endnotes:
1. Elie Wiesel, Night, Hill and Wang, New York, 2006, 120 pgs.
2. This can refer to soup or disinfectant being available at the entrance to the barracks. Obviously, Eliezer and his father dawdling by having their long conversation caused them to miss out on both shower and whatever was in the cauldrons. Just another example of the intended vague descriptions permeating this book.
3. In the book, “coffee” is in quotes signifying it wasn’t real coffee. I left off the quote marks in the original writing because of the quote mark signifying the end of the sentence. Poor judgement on my part, but whether it was real coffee or not wasn’t the focus of my attention in this critique. However, the sharp attention of the author of the Scrapbookpages Blog picked up on this and wrote about Wiesel’s failure to know that real coffee was not served in the camps. My apology to “Furtherglory” for misleading him and to my readers also. I have added the quote marks since reading the blog at Scrapbookpages Blog.
Category Featured | Tags: Tags: And the World Remained Silent, Buchenwald, Elie Wiesel, Gustav Schiller, Ken Waltzer, Night,
Social Networks: Facebook, Twitter, Google Bookmarks, del.icio.us, StumbleUpon, Digg, Reddit, Posterous.